For a successful search of metal objects in the ground is not necessary to understand the scientific principles of metal detector. However, it is useful to know in General terms how a metal detector works.
A metal detector is an electronic instrument which detects the presence of metal and informs us about it. Metal object, say a coin in the earth itself does not radiate and does not extradite its presence. To to detect, you need to expose it to the radio waves and to detect the secondary signal. All the detectors based on this principle, the Difference between cheap and expensive the models lies in the methods of emission of these radio waves, in methods of capture secondary signals, as well as in ways to inform you about the availability of the metal.
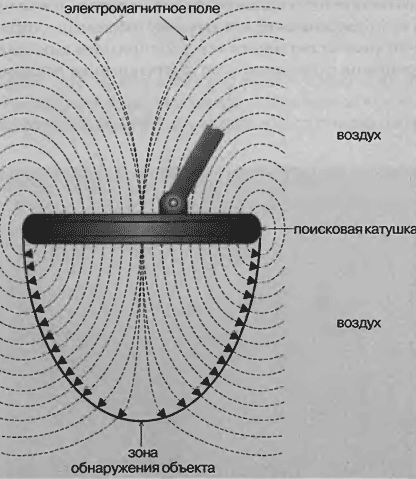
Fig. 12. The electromagnetic field of the search coil
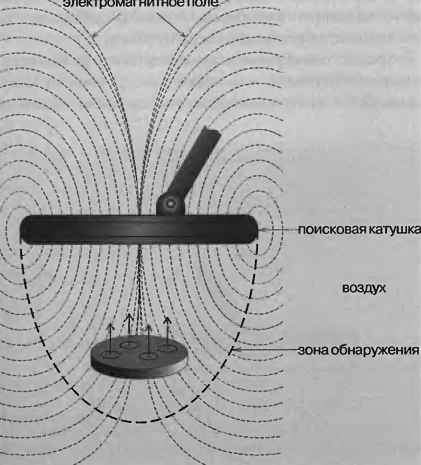
Fig. 13. The occurrence of eddy currents on the surface of metal objects, trapped in the electromagnetic field of the search coil
When you turn on the metal detector, search coil, an alternating the electric current that creates an electromagnetic coil around a field. This field passes into the environment, whether air, ground, water, stone, wood, etc. If this field is a metal object on its surface there are so-called eddy currents. These currents create their own electromagnetic field that weakens the field of the transmitting coil. The electronic circuit of the device with through the coil is sensed by the weakening of the field caused by the presence of under metal coil, and will inform you one way or another. More complex electronic circuits provide the best capture of the weaker secondary signals, they are treated more accurately. Therefore, such devices are time consuming in manufacture and are more expensive. However, they usually are able to find objects the greatest depth.
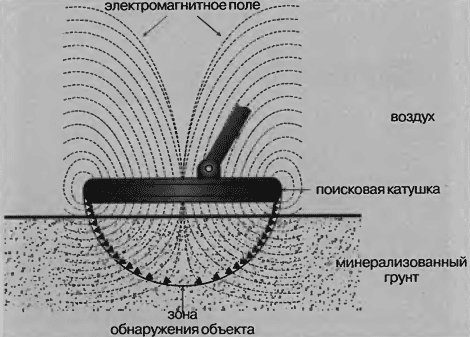
Fig. 14. The influence of salinity of the soil at the depth of detection
Eddy currents are formed on the surface of any electrically conductive materials metals, minerals, etc. non-ferrous metals more conductive than black metals and minerals. Therefore, eddy currents in them fade longer. The detector feels, which case the eddy currents decay faster, and on this basis can "say" you which metal - black or color - is under the coil.
Unfortunately, in some places the soil contains a large amount conductive minerals (magnetite, sodium and potassium) that are extremely undesirable because mask the presence of the metal, reducing its depth discovery. The iron minerals and salt are a major problem for manufacturers and users of metal detectors. Applying various filters, can greatly reduce the impact of the pound. Some devices have automatic ground balance, in others it is achieved manually by the operator, more precisely, if performed correctly.
In the literature there are the following basic approaches to the construction of circuitry metal detectors:
1. Method beat - BFO (Bcat Frequency Oscillation).
2. Method of induction balance - IB/TR (Induction Balance / Transmitter-Reciver).
3. Method of induction balance using very low operating frequencies - VLF/TR (Very Low Frequency/ Transmitter - Reciver).
4. Method of induction balance with spaced coils - RF (Radio Frequency).
5. Pulse method - PI (Pulse Induction).
6. Method breakdown of resonance - OR (OfTResonance).
Method beat - BFO
The measured parameter is the frequency of the LC oscillator including a coil search head. The frequency is compared with a reference, and the obtained difference the beat frequency is displayed on the audio display. The circuitry of the instrument is sufficient simple, the coil will netramet precision of execution. Operating frequency 40-500 kHz. The sensitivity of the BFO-appliances at low low stability and weak opportunities to build up from wet and mineralized pound. Method BFO was used in the detectors and foreign serial devices in the past 60-70 years century. Currently this method is popular among radio Amateurs and Dating in inexpensive devices of Russian producers. This may also include devices with direct frequency measurement, a well-implemented on microprocessors.
Method of induction balance - IB/TR
The search head is formed by two coils arranged in a single plane and balanced so that when a signal into the transmitting coil outputs reception there is minimal signal. The transmitter coil is often included in the circuit of the LC oscillator. The measured parameter is the signal amplitude the receiving coil and the phase shift between the transmitted and received sinusoidal signals. Such detectors have an operating frequency of 80-100 kHz. They can to detect small objects at relatively great depths (30-35 cm), however, they are useless when searching in highly mineralized pounds and marine beaches.
Method of induction balance using a very low operating frequency - VLF/TR
It was found that by reducing the operating frequency below 20 kHz can be rebuild from the influence of pound, depth of operation is thus somewhat reduced, but dramatically increases the stability and fade false signals. Such devices got the name of VLF/TR, which stands for the detector type the transmitter-receiver operating at very low frequencies.
VLF - method allows to construct a highly sensitive instrument with good discernment of metals by analyzing the phase characteristics. Circuitry devices are quite complex, the coils require precision balancing. On the basis of this method is now being built, the majority of serial devices, including computerized. Discrimination of objects and the ground in such the instrumentation is relatively simple using the phase-shifting circuits.
The principle of TR (or a variation of VLF/TR) provides the analysis phase characteristics of the signal, so these devices can easily distinguish between ferrous and non-ferrous metals, being rebuilt from the debris and soil. They have high sensitivity and the resolution, which depends on the diameter of the search coil - than it more, the deeper detection, but the harder to find small objects.
The disadvantage of such devices was the fact that the ground could not to run concurrently with discrimination and the operator using the switch should choose l for one or the other mode. Such devices were produced in the United States and England for 10 years until 1980, when they were replaced by the so called dynamic detectors.
In the late 70-ies of XX century American J. Payne has developed a scheme that allows conduct simultaneously and discrimination and ground balance.
The first devices of this type it was necessary to move very quickly to achieve an acceptable depth of their action, which was for the operator very tiring. Whiter late models (due to the complication of the scheme) is allowed to work already at lower speeds of movement of the coil without losing depth.
At the beginning of the 80s metal detectors have become heavy and difficult to configure. On essentially, one unit consisted of four different detector types. The American company Fisher Researh Laboratory responded to in a timely manner requests for the treasure hunters to make a more simple but not less sensitive the device and based on the latest achievements in microelectronics has developed the metal detector 1260-x with a self-tuning threshold, operating at very low frequency. He had only a few controls, and did not require any manual settings. It's lightweight, easy to use and sensitive to small targets the device, successfully acting in bad mineralized soils. Its modification 1266-x was produced until 2003
This detector has been called "dynamic", although, in fact, he refers to the type of VLF/TR. Previous static type detectors VLF/TR practically ceased to be, and all the leading companies quickly moved on production of the instruments, using the specified dynamic principle. Numerous small companies that failed to do so, were forced to cease to exist. Since then, the world is still l look at about a dozen firms producing metal detectors.
Method of induction balance with spaced coils - RF
This high-frequency variant TR, where the transmitting and the receiving coils to form not flat transformer, and spaced apart and are perpendicular to each other. Receiving coil receives reflected from the metal surface the signal emitted by the transmitting coil. This method is used in deep devices and is characterized by insensitivity to small targets, and the inability to distinguish between ferrous and non-ferrous metals.
Pulse method - IP
First developed in the USA for archaeologists, these devices have received the greatest popular among Amateurs of England in the late 60-ies, As in the devices, based on the principle of induction balance, pulse devices create electromagnetic field acting on the object, however this field is not valid all the time, and periodically going on and off (pulsing) many times within one second.
When the field on the object's surface induced eddy currents. When the off-field eddy currents gradually fade, although for a very short period of time. At this point, the coil acts as a foster antenna capture this fading signal. At this threshold of the device increases, indicating the presence of metal in the soil. Since eddy currents soil damped much faster and are not trapped by the device, a pulse metal detectors work effectively on a bad mineralized soils and especially on wet saline soils sea coasts.
The disadvantage of the pulse detector is a high sensitivity to ferrous metals and challenges discrimination. However, in some cases (for example, when you search for metal on the bottom of the sea), they exceed all other types metal detectors.
Method breakdown of resonance - OR
The analyzed parameter is the amplitude of the signal on the coil of the oscillatory circuit is tuned close to resonance with the applied to it by the signal from generator. The appearance of the metal in the coil causes or resonance or care from him, depending on the kind of metal, which leads to an increase or reduction of vibration amplitude on the coil. This method, as well as BFO developed by radio Amateurs.
Author: L. V. Bulgak






