Flashing LEDs quickly won the sympathy of hams. Ease the application compensates for some shortcomings, for example, relatively high the cost and the inability to control the frequency and duty cycle light pulses. Hams would not have been so, if not looking for non-standard options schemes the inclusion and use of the various electronic components. Did not remain without attention and flashing LEDs.
In the technical literature have already been published descriptions of devices which flashing LEDs were used as low frequency oscillators rectangular pulses, see, e.g., papers [1, 2]. Given that the composition of the flashing LEDs have a high frequency master oscillator with a frequency divider, not is easy to assemble the device by the circuit of Fig. 1, in which the flashing the led will simultaneously work as a low frequency generator with a frequency of pulse 1...3 Hz, and as a generator of a pulse train with a frequency of fill 100...350 kHz.
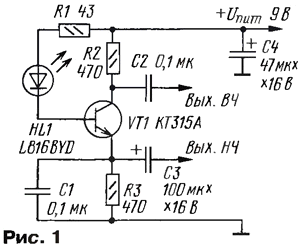
Bipolar transistor VT1 works as an amplifier-separator and high frequency low-frequency components consumed by the HL1 led current. At the conclusion the emitter of the transistor VT1 is allocated low-frequency component, the amplitude of the impulses here is about 2 V. the amplitude of the packets of high frequency pulses (Fig. 2) on the output collector of the same transistor is about 4 V. Unfolded waveform of the high-frequency oscillations of the pulses shown in Fig. 3. The capacitor C4 performs the role of locking on the food chain.
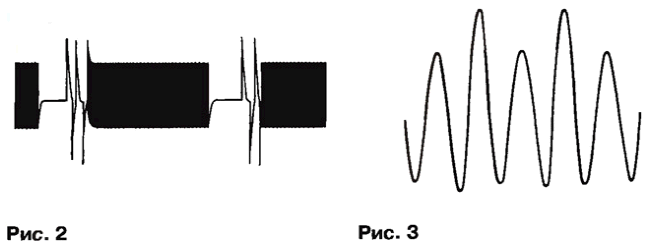
This generator has one interesting feature: if consistent with led HL1 to include a choke with an inductance of several tens of microhenry, the high-frequency signal output "painted" many high-frequency harmonics. This property can be used, for example, to check radios.
If the generator is executed according to the scheme Fig. 1, add the frequency divider, assembled on CMOS chip and two transistors, as shown in Fig. 4, get the audible tone generator pulses, reproducible high resistance dynamic head of BA1.
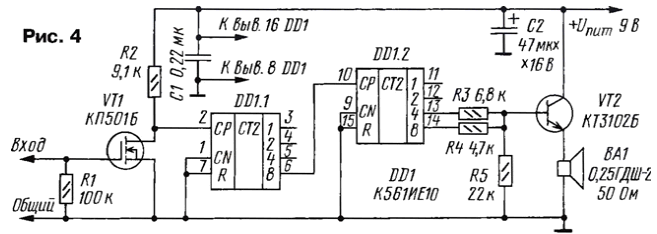
On the n-channel field-effect transistor VT1 assembled a high-frequency amplifier pulses of increasing amplitude to the level of the supply voltage. Chip DD1 type CIE consists of two four-digit binary counter. It included in such a way that at pin 13 is the pulse frequency is 128 times less than at the input (pin 2) and at pin 14 is 256 times smaller.
The tone and frequency of the beeps depend on the type and instance of the applied led.
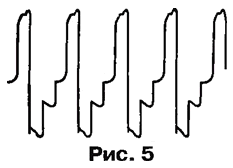
Cascade bipolar transistor VT2 is constructed by an emitter follower thus, non-dynamic head enters the four-level signal, the waveform of which is shown in Fig. 5. Changing in small steps resistors R3 and R4, it is possible to change the sound character dynamic head of BA1. The frequency of the beeps can be increased by connecting resistors R3 and R4 to other outputs counter DD1.2.
In place of HL1, the author used a flashing led light type L816BYD production company Kingbright yellow glow with a brightness of up to 40 MCD and the diameter of the housing 10 mm. you can replace any led series L816B...L796B... (8 mm), L56B... (5 mm) or, for example, matte red SuperBright L796BSRD/B. Suitable flashing LEDs and other manufacturers, but without a built-in high resistance current limiting resistor. The chip can be replaced CD4520AE, and with the change of the switching circuits - KIE, KIE. Bipolar n-p-n transistors - any of the series KT315, KT3102, CT, CT, SS9013, 2SC2001. Field - CPA, CPV, KRKA, CTA. Oxide capacitors - K50-35 or their imported counterparts. Nonpolar - K10-17. Resistors - C1-4, MLT, S2-23 S2-33.
Literature
Author: A. Butov, S. CORBA Yaroslavl region






