The territory of Russia is characterized by poor infrastructure, digital communication channels, especially land lines. By far the most common and sometimes the only means to communicate with high quality is a satellite link. On the territory of Russia has already deployed more than 200 earth stations operating with geostationary satellites "Horizon" that allows users to connect almost anywhere in the Russia. The article discusses how to more effectively use the bands transmission of long-distance and international lines of communication for the organization of access to satellite systems and networks with fixed (dedicated) TV or multiple access with time division multiplexing (Time Division Multiple Access - TDMА). Range of services - voice and data transfer.
The Russian market of telecommunication services is growing every year. Increases the number of companies, expanding the range of offers and services, reduced pictures. This is especially noticeable in large cities of Russia, where even now digital network one or more companies cover almost the entire territory of the city and anyone can get the whole range of telecommunications services, from installing a simple phone to access the Internet or other information and financial networks. If you need to link via a dedicated digital channel offices located in different cities or even countries, or to obtain access to the telecommunications network that are not represented in your city, we have to apply not only to local operators, but also to operators of long-distance and international communication (MMC).
Due to the relative maturity of earth stations on the territory of Russia created technical capability of the organization of long-distance and international digital channels by satellite. But the cost of the DS0 channel (64 kbps) the event will be a 4...7 times higher than that of the channel with the same speed, but within of the city. Such costs can go a few potential users. How to reduce the cost of long-distance or international parcel and thus to expand the range of users?
A possible solution is the unification in urban terrestrial wired networks several low-speed channels into a single channel DS0 (64 kbps) then send it to a satellite system. Said will significantly to reduce the cost of channel per user. To implement this scheme in two ways:
- for switching networks channels - the use of digital speech compression and Association of low bandwidth speech/data in one aggregate (combining multiple digital streams into one);
- for Frame Relay networks, ATM and H. 25 - use batch/HR switching with dynamic bandwidth allocation.
As this is solved by "Golden Line"?
The company's network "Golden Line" operating on the Russian telecommunications market for 5 years, one of the largest and most extensive transport network in Moscow. The main objective of the network - providing access to any telecommunications networks and services, in particular, to the operators of intercity and international communication (MMC) from any point of Moscow. To this end organises digital channels of communication with speeds from 1.2 kbps to 2,048 Mbps for connections with switching networks channels, X. 25 and Frame Relay, as well as up to 155 Mbit/s ATM technology.
The packet switching network X. 25 is widespread in the 80-ies and to still used in many departmental structures. Standard X. 25 was developed by ITU in 1976, he defines the interface between the terminal the user equipment and data transmission equipment network packet commutation. Through the support of technologies for the detection and correction of errors he ideal for data transmission via communication lines of poor quality. High-speed distributed network Frame Relay and ATM provides connection users to the operators MMS directly on these technologies. It is therefore, the effectiveness of these channels is achieved by dynamic allocation of bandwidth. In the article, this option organization lines MMS is not considered, as it is associated with the design network packet and personnel switching and requires a separate exposition. Should note that X. 25 network does not support the transmission of speech due to large delays.
Rapidly developing technology Frame Relay (frame relay) is modern Protocol switching channels, similar to H. 25, but using a simplified procedure to establish and verify the quality of connections. It is designed for operation at higher speeds (up to 34 Mbit/s) with low latency (see article V. Neumann "What is frame relay?" in the journal "Communication: means and ways to" No. 3, 4/1998. For Frame Relay networks, the quality of the connections, especially the speech transmission depends on many factors. This:
- functional characteristics of the user equipment, allowing to perform speech compression, echo cancellation and installation of the highest priority for speech frames;
- the dependence of the distribution of bandwidth-number of connections;
- the provision of the highest priority and minimum delays for speech transmission in public Frame Relay networks through which the channel. This specification standardized recently and not all supported equipment Frame Relay.
ATM (Asynchronous digital hierarchy) is a high speed transmission technology the information cells of a fixed size of 53 bytes, allowing us to provide of rooms with different types of traffic. ATM allows you to transfer and data water channel, i.e. to support and constant, and variable speed transmission information. ATM - the perfect universal media, which combines all the the advantages of networks of leased lines and data networks with dynamic the bandwidth allocation.
But in the world of global ATM network is still weak and too expensive for users. Therefore, this technology is not widely used.
For the category of users who need to transfer voice and data at low speeds a constant high quality of the connection, it is proposed use speech compression and consolidation of multiple channels of data/speech in one channel at 64 kbps. Here the technology of switching/multiplexing channels the most reliable and easy to implement, as most networks MMS use the same method of information transfer. The quality of the data in this is not changed, the same speech quality deteriorates slightly.
Let's discuss the technology of digital speech compression and the formation of the channel 64 kbps from several low-speed channels of voice and/or data.
Equipment used "Golden Line" for the implementation of this task, developed by firm Newbridge. An important advantage is that the compression and speech pulse-code modulation (PCM), and aggregation performs the same the device is a module called a digital signal processor (Digital Signal Processor-DSP). Each processor has 6,10 or 20 chains, each chain may to be configured as a compressor speech (Voice Compressor - VC) or as the unifier of low-speed channels (Subrate Merger - SRM). In each node multiplexer input/output can be set to seven modules DSP
Below describes the operating principles and standards that are supported by this equipment.
The voice compression
Like most firms in the telecommunications equipment, Newbridge supports two methods of compression of speech - own design - HCV(8 and 16 kbit/s) and standard, on the Recommendations of the technology Sector - ITU-T G. 728 - LD-CELP 16 kbit/s ITU-T G. 729 - A-CELP 8 kbit/s. Algorithms developed Newbridge, allow the most flexible and efficient bandwidth use the channel capacity of 64 kbit/s. however, the procedure was compression/decompressive can only be done on the equipment Newbridge. Using standard conversion algorithms of speech, for decompression you can choose any hardware that supports these methods. Quality compress speech at the speed of 16 kbps is equivalent to the quality of speed 32 kbit/s using adaptive differential im pulse code modulation (ADIM) used in telephony for long distance communication lines. And speed of 8 kbps with compression supports it "negotiating" quality (toll-quality speach).
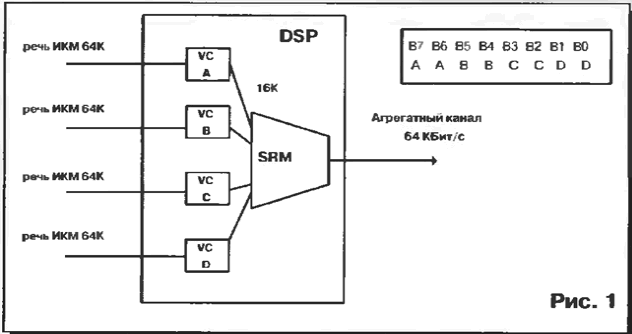
Thus, when using compression at the speed of 8 kbps channel speed of 64 kbps can contain up to eight voice channels, and at 16 kbit/s - up to four voice channels. The packing is compressed channels in the channel 64 kbit/s is performed by the method "transparent" adaptation speeds that do not require information about framing and signaling. The channel 64 kbit/s consists of the eight elements at the speed of 8 kbps with the notation from V7 to IN. Compress it at speeds of 8 and 16 kbit/s is placed in the appropriate the number of elements. Telephone alarm is transmitted within a user-defined information. This method of signaling is called "in-band". In Fig. 1 shows a diagram of link aggregation and their placement in the aggregate channel 64 kbit/s.
Association of low-speed data channels
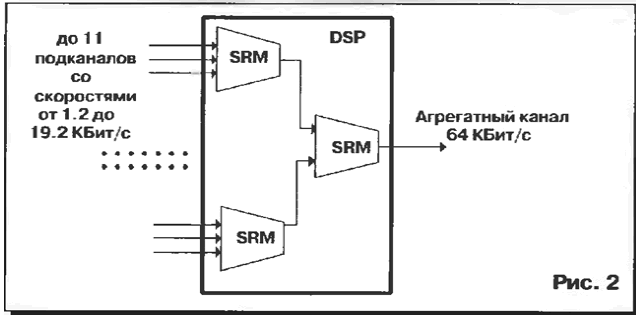
Association of low-speed channels at data rates from 1.2 to 19.2 kbps according to the same principles and the same equipment as the Association voice channels. Data are fed to the combiner low-speed channels SRM, where information from multiple users is grouped in a single channel 64 kbit/s.
Firm Newbridge offers two methods of aggregation:
- self - HCM (High Capacity Multiplexing - high-performance a multiplexing) that supports a very high ratio (98,75%) the use of bandwidth for digital transmission, and multiplexing synchronous and asynchronous data channels and, if desired, enable user data bits and synchronization States of control signals;
- standard - 50 and H. DDS.
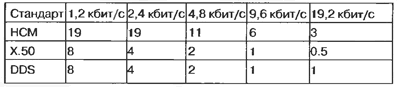
H. 50 - European standard multiplexing, developed in accordance with ITU-T describing the mechanism of combining multiple simultaneous low-speed channels into a single channel of 64 kbit/s Standard adopted for determining interface between public data networks at the international site.
DDS - North American standard similar to H. 50 developed by AT&T and support multiplexing synchronous' and asynchronous channels data. The table shows data on the number of low-speed channels, that may be transmitted in the channel 64 kbit/s for one cycle of the frame 2,048 Mbit/s (the interface described in Recommendation G. 703 ITU-T).
When compared, it is obvious that the use of a method of multiplexing HCM much more effective than the others.
The scheme of multiplexing is presented in Fig. 2.
Access to operators MMS
The above methods for the effective utilization of bandwidth 64 kbit/s allows to develop various schemes and projects to connect users to the satellite networks, multiplexing methods in the channel 64 kbit/s can be combined and discussed, and data.
In Fig. 3 shows a scheme of the connection of users to the ground node satellite communications.
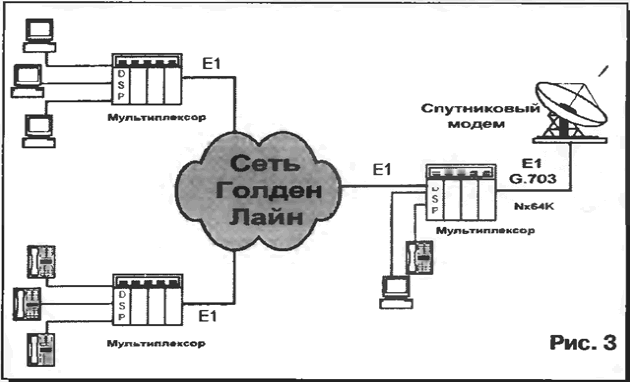
The interface between the multiplexer I/o satellite system can be selected from any described in the ITU-T V. 24, X. 21, V. 35 G. 703. In if you use the standard G. 703 you can connect up to 30 aggregate channels at 64 kbit/s in one thread 2,048 Mbit/s. These interfaces are used in private and public data networks with time division channels and are available in almost any telecommunications equipment - switches, multiplexers and routers. Satellite system or modem must have modules for connection to the terminal equipment with data the above interfaces. Such systems can be, for example, custom VSAT satellite station-NEXTAR company NEC or low-speed satellite modem SDM-100 firms EFData and DMD2401 Radyne company.
In conclusion, we note that the effective bandwidth usage channels MMS could be useful to many satellite operators for the reduction of tariffs on services and thereby attract more customers. Such a scheme is implemented successfully in a joint project of the British Telecom and Golden Line" for the provision of voice channels with compression on speeds 8 and 16 kbit/s the Moscow banks for IPO on the London stock exchange. Using the technology of voice and data transmission in one or two channels of 64 kbps seems to be an optimal solution for corporate networks companies with offices in different cities and countries.
Author: S. lariushkin, Moscow






