Many motorists know that it is enough to see a small scratch - and rust begins to engulf the car. And to fight it very hard. Which only come up with any tricks motorists - various coatings, mastics, antibodies... but here's the problem: in order to handle properly all of the most affected places, sometimes have to disassemble the entire car. Such an operation takes time, and requires constant monitoring. In addition, in the operation process is the gradual destruction of the coatings. Due to vibrations when driving cracks will appear, under the blows of stones or sand the paint chip. So it is understandable desire of motorists to purchase a miracle device, once spent, and will forever defend the body from rust.
Method of cathodic protection against corrosion has long been used on a variety of objects. For example on ships set special protectors, which, when dissolved in sea water, provide protection to the hull. Underground pipes before laying treated with a rust inhibitor and is wrapped with a special tape. At a certain distance from the pipeline is buried anode (electrode) - a metal disc, which connect plus DC source, and the tube itself - minus. Due to the potential difference between the electrode and shielded metal in the circuit formed of the electrolyte (moisture, salt, etc.) is current. At the anode there is a release of electrons - oxidation reaction, and the resolving process of the cathode is terminated [1, 2].
During the cathodic polarization of the metal is necessary to report a negative potential at which the oxidation becomes thermodynamically unlikely. For iron and its alloys full corrosion protection is achieved at a potential of 0.1...0.2. Further, the shear capacity has little effect on the degree of protection. Protective current density should be in the range of 10...30 mA/m2.
In addition, over time on the metal due to the concentration polarization of oxygen there is an additional bias potential to the negative side that allows you to periodically turn off the device when it is car repairs, battery charging, etc.) [3].
The device corrosion protection consists of an electronic unit and a protective electrode. On the housing of the electronic unit is placed a light display of the device.
The device allows you to maintain the value of the potential wet areas on the surface of the body at the level necessary to a complete stop and stop corrosion processes due to the destruction of the protective electrodes.
As a protective electrodes (anodes) can be used as a collapsing materials (stainless steel, aluminum), requiring replacement after 4 to 5 years...and non-destructive. As a non-volatile electrodes can be applied carboxyl, magnetite, graphite or platinum. Protective electrodes are rectangular or round plates with an area of 4...9 cm2.
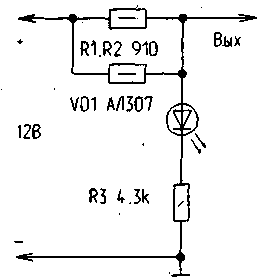
The figure shows the diagram of a simple anti-corrosion device that can successfully cope with the phenomena of corrosion. Of course, in its simplest form, the device of cathodic protection may consist of shield electrodes and wires connected directly to the "plus" terminal of the battery. However, it is difficult to control a possible short circuit of the electrodes with the car body and its work in General. For this purpose the unit circuit of the voltage divider R1, R2, R3 led VD1, which is in the working mode will be lit solid, consuming little current from the battery (about 2 mA).
If one of the protective electrode is shorted to the vehicle body, the VD1 led stops glowing. In this case, you must find and fix the circuit. If the humidity of the body led VD1 may slightly change its glow, indicating that the cathodic protection work. In addition, this device has high reliability because it gives short circuit of output with a body surge current not exceeding 30mA 25....
When installing and mounting the unit, remember that:
- one protective electrode protects the area with a radius of about 0.25 to 0.35 m...;
- shield electrodes are installed only on the places protected with a paint coating;
could use epoxy glue or putty on its basis;
- outer side shield electrodes (no soldering) cannot be covered with mastic, paint, adhesive or other insulating coating.
The electronic unit is installed in any place of the car and joins the General scheme of the electrical vehicle. Thus it is necessary that the electronic unit is powered on even when the power General vehicle's electrical system.
In General, the device consumes no more than watch the car and ensures long-term efficient operation even with a fully discharged battery.
Literature
1. Krasnoyarsk, V., E. V. Zobov cathodic protection facilities and equipment from corrosion. -1981.
2. Lublin E. J. Electrochemical protection against corrosion. -1987.
3. Turchin V., Bondarenko A. Current protects against corrosion. At the wheel.-1993.-N 12. -S. 23.
Author: P. Bialiatski, Novosibirsk region, Berdsk; Publication: N. Bolshakov, rf.atnn.ru






