Introduction
The wide spread of mobile communication on 27 MHz acutely raises the question about the antennas for such communications.
This question is complicated by the fact that the use of quarter-wave antennas, the length of which is for the range of 27 MHz to 2.7 meters, in many cases unacceptable. The use of shortened antennas is associated with a number of specific issues in the popular literature are not considered, but the ignorance which the effectiveness of SV-communication can significantly deteriorate.
For portable CB radios are mainly used unbalanced whip antenna. This is due to the fact. what other antenna types just almost impossible to use with this type of radio stations.
1. Work electrically short antennas for portable stations
Electrically short antenna consists of the antenna, which vklyuchav radiating element and of the elements of the system of adjustment and system grounding. In accordance with the total resistance of the antenna Ra consists of a resistor pin (Rш) and resistance to ground (Rз) (Fig. 1).
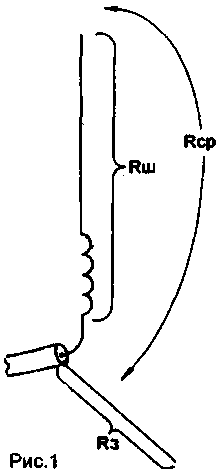
Included in the formula and "drag resistance" RS. which decreases with an increase in the number of counterweights and the length of the antenna.
Ra=Rш+Rз+Rcp
Useful RF energy is dissipated in Rш, so you need to strive to reduce the quantities Rз and Rсp. In the General case with the help of special methods, you can measure the resistance "earth", but in practice can be taken that the resistance of the hull CB radio length 20...30 cm, used as a counterweight, the length of this formula is equal to at least 150...300 Ohm.
Contact with the human hand insignificant change well size. But the connection of quarter-wave resonant counterweight length of 2.7 meters reduces the resistance of the earth Rз. The counterweight reduces the resistance Rз approximately to a value of not more than 50...60 Ohms. and if there are three or four counterweights can be considered Rз negligibly small value 5...10 Ohm. The resistance of the medium is determined by the interaction of the probe with its antenna "ground" system. If a full-sized quarter-wave whip antenna this interaction occurs in a large space and has a small due to this variable, but in shortened antennas, electromagnetic interference short antenna short counterweight happenin g in a limited volume of space. Moreover, any interference in this volume significantly changes the resistance of the medium, consequently, has a significant influence on the parameters of this antenna system. And in this antenna system with shortened elements of a significant increase in one of them. for example pin up to the size of a quarter-wave, or counterweight, does not cause significant reduction in Rcp. And only increase (i.e. elongation) as pin and counterweight causes a drop in Rcp.
Already from this we can conclude that the resistance of a short antenna SV-station - value is not a constant but a variable which, in particular, depends on the position of foreign objects (including the operator) relative to the antenna.
In the General case of well-coordinated antenna under the influence of these factors can fully rassoglasovaniya.
From this it follows that the output stage of the transmitter SV-radiostyle must be constructed so that such a mismatch does not significantly affect its operation, and to eliminate the causes of the error output stage continued to function normally. This requires that the output transistor had 3...4x the power reserve. Also needed is a compromise matching circuit of a P-loop. to allow operation in an integrated variable load. It is necessary to eliminate self-excitation when changing the parameters of the antenna. Already these requirements. presented to the output cascades of ST portable stations, show that the approach to their design is extremely serious. For mobile car radio running on a stationary car antenna requirements for RA are much lower. This is due to the use as a counterbalance to the chassis of the vehicle, which is good "earth" for CB antenna. The pin used for automotive CB antenna. has a length of about one meter, and in many cases longer. This creates the preconditions for the work of a car antenna with a much bigger effect than the antenna of the portable station. It is significant that in the interaction zone displacement currents in the system "pin of the antenna - opposed" no foreign objects, making Rсp for such antennas more stable than in portable stations.
From all available types of CB antennas for portable stations can be divided into two groups - resonant and non-resonant antenna. Among short whip antennas from the group can distinguish resonant helical antenna and the whip antenna, elongated inductance. Among the non-resonant whip antenna it is advisable to use only one type - short pin in the composition of the output of the resonant circuit. In this case, the pin contour is a capacitor having a distributed capacity.
2. Helical antenna
A helical antenna can be regarded as an open spiral resonator [1]. In this case, the antenna itself is a spiral resonator, the circuit matching circuit of the transmitter - the continuation of a spiral resonator and is included in the circuit of its excitation, and the external space can be regarded as infinitely remote screen (Fig. 2).
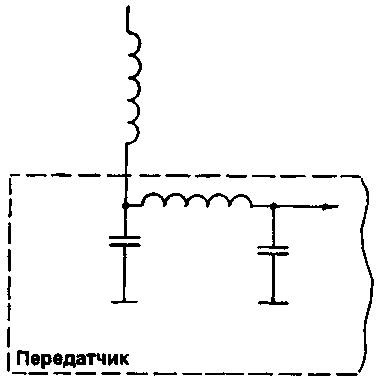
Fig. 2
The validity of these assertions can be easily checked in practice. So, when you change the parameters of the matching circuit changes the resonant h ut antenna system. Even a very slight change in the terminal capacitance of the antenna will change its resonant frequency [2]. And spiral antennas are highly susceptible to foreign objects. Already the approach of the hand to a distance of 20 cm leads to misalignment of the antenna with the transmitter, because the changes limit the capacity of changing its resonance frequency. Here it is appropriate to carry out the adjustment according to the method proposed in [3]. It is that the helical antenna set up so that the hands on approach (or because of other massagesome influence) the field strength of the signal increases and then decreases. In this case, the dish is not exactly in resonance, and a little away from him.
As shown by the field strength measurement, in this case the field strength is about 85% of the field strength at the exact resonance. But when testing the radio with the antenna tuned to resonance, and with an antenna that is configured to slope characteristics of the antenna, its advantages are obvious. So, when you use a station with a resonant antenna in the process of radio communication when approaching the antenna to the man there were significant fluctuations of the field strength. When using the same radio with an antenna that is configured to slope characteristics, massagesome human influences manifested much weaker and fluctuations in the field strength was negligible. Accordingly, it is possible to recommend to configure a helical antenna according to the method proposed in [W]. Only in the case that a helical antenna operates in conditions where it is possible influence massagesexy factors, you can configure the antenna to the maximum field strength.
When measuring the field strength provided by the helical antenna and a whip antenna with a lengthening coil, it was found that tuned in resonance with the whip antenna length not less than three times greater. than the test helical antenna, provided the same field strength. From this we can conclude that in portable stations the most optimum choice of antenna is a spiral, which is stronger and simpler in design than the same but the parameters of the whip antenna. In this case, you must activate that in this case short case is the best radio station "earth" for a helical antenna than for the same pin settings. But spiral antenna. providing large field strength, a prerequisite for unstable operation of the transmitter.
Indeed, in the experiments it was found that the same transmitter, steadily working with external antenna power cable, when connecting the helical antenna was excited. Only a more thorough screening and tuning of matching circuits to the transmitter with a spiral antenna without self-excitation.
Helical antenna, as well as girevoy, you can configure the frequency with shortening capacity and lengthening the inductance. The use of capacitance increases the resonant frequency of the antenna, and the use of inductance lowers it. In this case, to improve the efficiency of the antenna is required to lengthening the coil was probably smaller inductance, and shortening capacity - the greatest possible value. The use of such setting items allows you to use a helical antenna in a wide frequency range, since the top depending on the performance and the quality of matching the bandwidth of a helical antenna is small and is 200...300 kHz in the range of 27 MHz.
There is another very important point when using spiral antennas. When you connect like this ananny over coaxial resonant frequency due to the introduction of the reactivity of the cable in the complex impedance of the antenna and, consequently changing it. changes and needs to adjust.
When you build a helical antenna, for that matter, any other shortened antenna, you should pay attention to another feature of this antenna system consists in the fact. connecting a quarter-wave counterweight slightly change the resonant frequency of this antenna system. This can be explained by the fact that opposed to having their Rз, changes Rсp. There are also changes to capacity "antenna space". Expanding the bandwidth of a helical antenna is about 1.5...2 times by reducing its q-factor and at the same time - due to more efficient radiation. Basically, the experimental study of the resonance frequency of a spiral with a quarter-wave counterweight does not extend beyond the bandwidth of the antenna. At the same time, the intensity of the field with a quarter-wave counterbalance increased by at least twice.
Helical antenna should be connected as short as possible wires to the output matching circuit. This helps secure the necessary bandwidth and minimum spurious emission line connector.
3. Practical design of spiral antennas
Below we discuss practical design of spiral antennas presented in the literature in recent years. The parameters of the antenna were measured using antennashop.
Helical antenna design shown in Fig. 3 was published in [4]. Testing this antenna showed that this quarter-wave antenna is on the 21 MHz band. Indeed, together with quarter-wave resonant counterbalance the resistance of the antenna here was of the order of 40 Ohms. with a small reactivity.
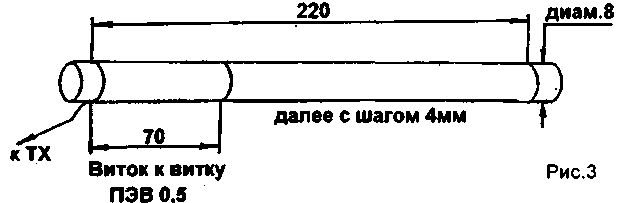
When you connect the antenna to the transceiver with an output of 40 watts through a coaxial cable with a length of about ten meters and the antenna are positioned in the window opening managed to spend a few links to 21 MHz with RST56-58, which further strengthened my opinion of its true resonance. But by tuning coils and capacitance, as shown in [4] managed to establish that in the range of 27 MHz possible resonance corresponding to the equivalent length of the antenna is half the wavelength.
The bandwidth of the antenna at 21 MHz band was 200 Hz, in the range of 27 MHz to 250 kHz with a quarter-wave counterpoise.
Spiral antenna whose data is shown in Fig. 4, refers to a quarter-wave antennas. With superstructure pin it can be rebuild in a wide range from 26 MHz to 35 MHz. In the range of 27 MHz input Impedance of the transceiver was 130 Ohms and a bandwidth of 650 kHz. With a quarter-wave counterweight 65 Ohms. Bandwidth was 800 kHz. resonance was shifted by 200 kHz up. It should be noted that this method of adjusting the resonant frequency of the antenna though quite good in its simplicity and efficiency, but reduces the quality factor of spiral resonator and, consequently, reduces the efficiency of the antenna. This is reflected in the decrease of the field intensity and the extension of the bandwidth of the antenna.
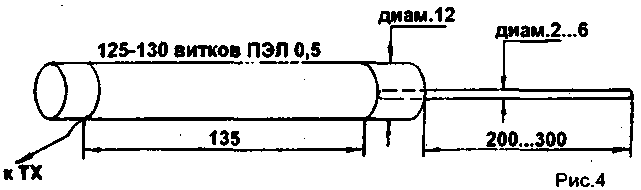
The spiral antenna is shown in Fig. 5 [5]. when tested on antennashop showed no resonance in the range of 27 MHz and showed quarter-wave resonance in the range of 21 MHz. In conjunction with quarter-wavelength edge of the resistance here was 25 Ohms bandwidth of 250 kHz. But when using matching systems are listed radios [5], it was found that in fact in the range of 27 MHz is achievable resonance. Obviously, here the resonance of the antenna is not at the expense of her work as a quarter-wave resonator, and as the P-circuit distributed capacitance. In this case, the helical antenna is equivalent to the system of P-circuits included in the output of the transmitter, the capacity which is the capacity of the antenna to the ground. The radiation occurs due to the settings in the resonance of the whole system U-contours of the transmitter. However, field strength measurements showed that in this case the use of a helical antenna is inefficient. The same field strength can provide tuned in resonance with the assistance of the extension coil whip antenna with a length of only 1.3 times more than the length of this helical antenna.
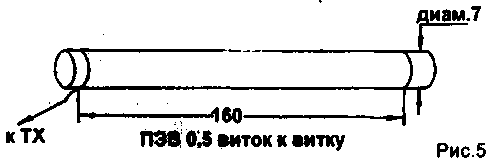
Helical antenna shown in Fig. 6 [6], showed that the input impedance at the resonant frequency range of 27 MHz 110 Ohm corps station and 40 Ohms with a quarter-wave counterpoise. The bandwidth with the building of the station was 300 kHz. with counterweight - 450 kHz. Due to the fact. that the upper part of the wound with discharge, the influence of human body on the setting of this antenna is not as strong as in the case of continuous winding. Connecting a quarter-wave counterweight changed the resonance frequency of 200 kHz up.
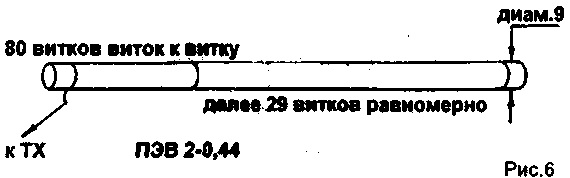
We investigated the antenna used in radio type "Kolibri-M2". Its construction is shown in Fig. 7. In the range of 27 MHz this antenna showed a resistance of 100 Ω and a bandwidth of 300 kHz with the shell station, and a resistance of 47 Ohms and a bandwidth of 200 kHz with a quarter-wave counterpoise. Connecting a quarter-wave counterweight changed the resonance frequency of 120 kHz up. It is the antenna shown in Fig. 5 and 6. provided the field strength. comparable to the field strength developed by the whip antenna with a lengthening coil, with the length of the pin, three times the length of this helical antenna.
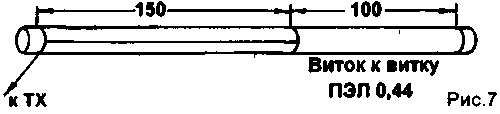
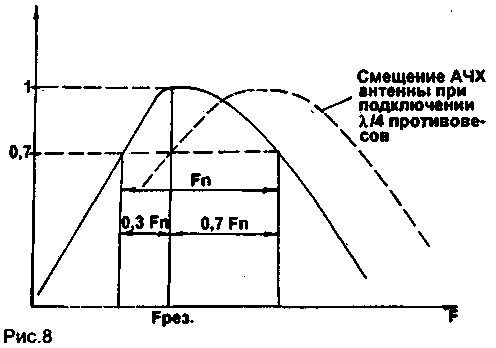
A practical view of the AFC the last two antennas shown in Fig. 8. From this figure it is seen that the frequency response of the antenna is unbalanced. When connecting a quarter-wave counterweight AFC somewhat mixed up about. 100 kHz for the range of 27 MHz, the bandwidth of the antenna allows it to operate in the ne channels. Knowledge of the frequency response of the spiral antenna allows you to properly configure it - not in the middle of the operating range, and slightly higher.
4. Production and tuning of helical antennas
In the literature it is recommended to perform a helical antenna on a plastic core coaxial cable. Indeed, this is the best option material for such an antenna. Cable for manufacturing a helical antenna, it is desirable to use 75 Ohm, because it usually contains a single inner conductor, which can easily be pulled out with pliers, while holding the cable at the other end in a Vice. If you use for the frame antenna 50 Ohm cable that usually has a center conductor consisting of several copper wires can be difficult to remove them.
The simplest way is to heat the conductors, passing through them a current of 50...100 And with the help of any powerful current source. and then quickly pull up.
Plastic frame has after Stripping rough surface, which facilitates the winding of the wire with tension. It should be remembered that the spiral antenna is a high q system, and if it is done carelessly, under the influence of the temperature of the resonant frequency may go beyond the range for which it is configured. In the study of spiral antennas found that their resonant frequency is shifted by 50...80 kHz up when cooled to a temperature of -15°C. the Antenna must be wrapped tightly with electrical tape to avoid shifting of the turns. and thus changes the resonant frequency. Fits flexible PVC duct tape. Adhesive tape type "Scotch" is not appropriate for this purpose because of its stiffness.
It should be noted that a helical antenna is an unbalanced system. K. the transmitter should be connected to the same end, which is indicated in its description. When connecting the antennas shown in Fig. 6 and 7, the other end, they will have quite different resonances, far ustawie from the range of 27 MHz. Even with a change of end connections like this, it would seem. symmetric antennas as in Fig. 5, there is a shift of its resonance due to some asymmetry of the execution of the antenna.
Structurally, it is convenient to perform its end connected to the transmitter, using the connector SR-50 or SR-75. by zaplavlenie back of the plastic base of the antenna. From the metal frame of the connector prior to the winding of the spiral shall not be less than 12 mm. In the manufacture of the antenna does not necessarily seek to use the foundations specified diameter. Retreat 2...3 mm is quite acceptable. For example you can use instead of 7-mm plastic bases 9 mm, it can be also used instead of 12 mm. Although the parameters of the antenna are thus changed, it can be set in the range of 27 MHz.
Adjust the antenna, as indicated in the description, by unwinding turns from tighter winding. In Sluchak manufacture of all of the antennas described here was able to configure the range of 27 MHz by unwinding part turns. meaning they have been pre-designed for a resonant frequency just below 27 MHz. For efficient operation of the antenna should have good ground station, for example a metal case. If there is none, you need to lay in a convenient location for the entire length of the station wide copper or aluminum foil. Such a counterweight gives an increase of the field strength by about 15...20%, which is about the same increases the communication range. In some cases it helps to remove the excitation of the transmitter.
The dimensions of the helical antenna can be considered optimal if its length is approximately 20% greater than the length of the hull of counterbalance. If the antenna is smaller than this value. increases the influence of the human body and other foreign objects. Further increase does not cause the same increase of the field intensity, it is easier to use a quarter-wave counterweight to increase the communication range.
Continued
Author: I. Grigorov (RK3ZK, UA3-113); Publication: www.cxem.net






