The article considers the principles of creation and practical design multiband vertical antennas with top diet. They are especially convenient for work in the field or in expeditionary conditions, but nevertheless can be used in the home "the shack", occupying little space and providing good settings.
The problem of creating a simple and effective multi-band antenna still care almost every shortwave. Most often, attention is attracted to design of vertical antennas because they take up little space, are easier to installation and optimised for DX-links the chart orientation (LTO): a zero in the Zenith direction and a maximum in the direction of the horizon and the lack of azimuthal orientation, allowing to carry out radio communication with correspondents in all directions.
Many of the known design verticals, fed from the bottom, suffer the disadvantages associated with the inefficient use of high-frequency ranges the entire height of the mast and the difficulty settings bandstop circuits (ladders, or other devices that are located at a considerable height and, actually, converting a multiband antenna. In the first part of this article considered, what are the advantages and convenience appear when you shift power point up, along the radiating conductor vertical antenna. For brevity let's call described the antenna GDP - vertical upper power.
Designing GDP
Along the radiating conductor of the vertical, just like any other antenna, establishes a standing wave of current is zero at the top, so power point cannot be placed near the top is the input impedance will be too great. Shifting the feed point down from the top, we find ourselves in a place where the current is already significant, and the voltage is less than on top, so the input impedance (equal to the ratio of voltage to current) is decreased. In the Central feed point conductor of the coaxial feeder attach to the top of the vertical, and braid anywhere... let's attach will not. Then the current will flow from power point on the outer surface of the braid, and in the same direction as the at the top of the vertical.
This concept is described in the article [1], in the third part, referring to Fig. 19. There is current on the braid is proposed to use for better days. Following these recommendations that will make the current part of the basic braid, the radiating current. Note that the currents on the outer and on the inner sides of the braid of the feeder does not related due to the very small thickness of the skin layer in the conductor, they only equal to each other at the top cut braid.
In Fig. 1, and schematically shows the projected vertical, as in Fig. 1,b - the current distribution in it. The feed point And the marked circle (graphics program MMANA). Here, the center conductor is connected to the upper part of a length of 3 meters, and braid is left free. The sinusoidal current distribution will continue on the upper part of the vertical antenna and the braid. At point b the distance of the half-wave from the top of the vibrator antenna in the range of 10 meters formed by the current node (see the leftmost graph of current distribution in Fig. 1, b). At this point, be to put a band-stop circuit to stop further flow of current down braid.
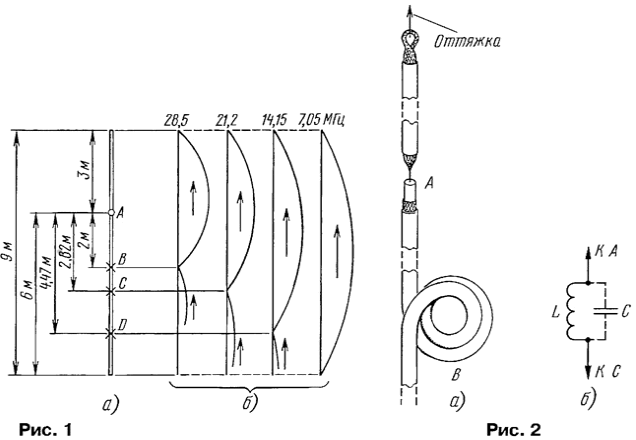
The contour of the easiest to do in the form of a Bay of the cable without disturbing the integrity of the latter [2, 3]. We've got vertical band antenna 10 meters. It the design shown in Fig. 2, and. Antenna can run entirely from coaxial cable, using the top only the top braid cut cable. To connect or not with her inner conductor - care current still will flow only on the braid. Hang the antenna on a dielectric procrastination (thick line) to a tree branch, etc., it is only necessary to provide durable mechanical bond lengths of cable at the feed point And, as the center conductor is unlikely to bear the weight of the entire feeder and "balun".
Another option is to attach the antenna to the thin mast from dry spruce or pine (raw the tree makes a noticeable loss) or to the fiberglass rod. In this case the upper part is advisable to do from the metal tube.
Let us return to the circuit. Bay cable has significant inductance L and same time, the capacitance between the individual windings, the main role is played by the capacitance between the first and last round. The total equivalent capacitance closes With the Bay. So way, Bay cable for RF currents represents a parallel circuit, circuit equivalent to that shown in Fig. 2, b. Frequency settings can be varied by selecting the number of turns, the diameter and the stacking order - positioning the first coil is closer to the last mu, increase capacity and lower the frequency To adjust the frequency of 28.5 MHz only three turns with a diameter of 13 cm [3]. Interestingly, even the incomplete locking of the current on the braid the remaining current is below circuit will flow in the same direction as in the antenna - because the circuit inverts phase, due to the findings of the equal and anti-phase oscillations. Therefore, the remaining current at the bottom of the cable will not spoil days, even improve it.
Now, outlined the important dignity of GDP: the first is to set the antenna (select the diameter of the cable and its status with you saute vertical) below, five meters below the top point and the second point of power And can be placed anywhere on the vertical, achieving the desired input resistance antenna, no additional balun is not required.
Focusing on available 75-Ohm-tion cable television, a little appropriate to move the feed point And down relative to the middle of the half-wave current, the input resistance increases a little in comparison with the resistance a half-wave dipole, fed in the middle (73,1 Ohm for infinitely thin and somewhat less for the vibrator of finite thickness). Considering frequent the length of the dural pipes, equal to 3 meters, and was chosen as the length of the top. Why not 2 meters? To make the antenna work better on others ranges.
In the range of 15 meters the path To not configured already in resonance and these frequencies only some inductive reactance (see Fig. 1 in [3]), as how would lengthening the coil. As a result, the length of the wave decreases from 7.1 to 5,82 m (see Fig. 1). At this distance from the top of the vertical will be the current node, and here turn on the second bandstop circuit, tuned to a frequency of 21.2 MHz (middle frequency range of 15 meters). Continuing the process further, turn on the third contour D already configured on the frequency of 14.15 MHz (mid-band 20 meters), and we will see that for the range of 40 meters length of our half-wave vertical antenna was only 9 meters.
Such a significant shortening in the range of 40 meters occurred because joint the influence of the circuits b, C and D, which are at a frequency of 7 MHz inductive resistance and serve as "lengthening" coils. When shortening of the half-wave vibrator the radiation resistance referred to the antinodes (the maximum) current falls. But the feed point And at least reduce the frequency turns out to be all above in relation to the maximum current and the input resistance equal to the resistance radiation converted to the feed point increases. These two processes in largely compensate each other, and the input resistance remains approximately constant during the transition from range to range.
All this design was easily and quickly done with the help of a program MMANА, but after some optimizations (not sure that still it is impossible to improve) turned out the antenna is depicted in Fig. 1. The input impedance of the antenna in the range of 10, 15, 20 and 40 meters were, respectively, 78, 67, 69 and 61 Ohms at zero reactance, which provides good agreement (CWS less than 1.2 at the center frequencies of the bands). In the calculation were as follows the values of parameters of equivalent circuits (frequency, inductance, capacitance): - 28, 5 MHz, 1,6 mH, 19,5 pF; With Of 21.2 MHz, 2 mH, 28 PF; D - 14,15 MHz, 3,2 mH 43 pF. Maybe the main advantage of the designed vertical and Hori - it requires no ground or radials.
It remains to decide how to move the feeder further down from the lowest point of the vertical (see Fig. 1, a). We already know - to wind another Bay of the same cable to formed a circuit that is configured to 7,05 MHz. Another possible solution - a little below the circuit D to attach to the braided cable is three or four short (length about 1.5 m) horizontal or inclined radial. They will bring electrical length of the antenna to the wave in the range of 40 meters. Short radials do not eliminate the need for band-stop circuit, but now it will be located right under the connection point of the radials. Inductive coupling of this circuit loop D (because now they're close) undesirable. Instead of the circuit in this embodiment suitable chokes wound around the same feeder on the ferrite rings.
The process of setting up the GDP seems simple and obvious enough. Begin from the high-frequency range of 10 meters. Picking up the density (diameter) and small within the height position of the Bay To achieve acceptable SWR on that band. Securing the Bay of tape, move on 15-meter range and repeat the same operation with the Bay, not touching the tuned circuit is V. And so on until you have configured all the antenna at all ranges.
Antenna cable, for example, RK-75-4-11 especially good for field conditions. It and configured,can be in the field, if the transceiver is equipped with a SWR meter. In inpatient GDP, probably can be made of duralumin tubes, separated by dielectric inserts in areas b, C, D and at the lower end. On top of the inserts placed the coil bent of soft copper or aluminum tube (tape). Capacitors circuit must be high voltage, since the footprints are placed in the voltage loops. The cable in this case should be inside of all pipes right, but avoid the current on the braid on it it is necessary to put some ferrite rings and the lower edge of GDP to reel the dams throttle or more ferrite chokes on the big rings diameter. This option is GDP not counted and not the wearer.
In conclusion of this part is another proposed GDP. To make the antenna to operate in the range of 80 metres, at the bottom point of the vertical (see Fig. 1, (a) it is necessary to install a protective circuit tuned to a frequency 7,05 MHz, and below the braided cable (lowest pipe in the stationary system), ground or to connect with a system of radial wires with a length of 20 m. Then the antenna will work on frequency of 3.6 MHz shortened as the inductance of a quarter-wave GroundPlane with raised by power point.
Portable Dualband GDP
The first practical variant of the GDP was made urgently, "on the knee", when there was the need to deploy the radio magazine "Radio" at the exhibition NTTM-2002. Huge pavilion with openwork metal slabs and the metal fittings glazed walls precluded the placement of the antenna inside of the building due to the complete shielding of signals and high noise level. Fortunately, managed to install a vertical antenna on the roof of the ventilation box, and skip the cable in the ventilation shaft.
A year later, a few days before the opening of the exhibition "Expo-Science 2003" (see "Radio", 2003, № 8, the first cover), fate gave unpleasant surprise. The similar roof of the pavilion, where they talked about the show, was a flat field, bigger than a football, covered with roofing material. To pick it, to drive nails, hooks, etc., as well as to use the ventilation shaft, it was strictly forbidden. The speech could go only about free-standing antenna with feeder, descending along the outer wall and entering the building through a crack in door. The situation seemed hopeless, but a few hours of simulation with the program MMANA and two nights of revision of GDP solved the problem.
Needed at least two ranges: 20 and 40 meters. On them and was designed antenna. In a disassembled and folded it fits in the package with a diameter of 30 and a height of 160 cm, it is easy to carry with one hand (not weighed, but Bay cable many times heavier) and brought to the exhibition in the subway. After an hour and a half spent on installation and solving organizational problems (feeder wiring, network, table, etc.), it provided a connection with Siberia, Western Europe, and then a more distant correspondents.
A sketch of the antenna shown in Fig. 3. The upper part of GDP above the point of supply And made of three duraluminium tubes inserted into one another (medium ski pole, the upper is very light and thin). Training nutrition And loop radiating element 1 serves as a braided cable, its Central conductor connected to the upper part of the antenna 2. Below loop braided cable connected by four radial 3, made of thin-walled steel profile rectangular (window curtains). The outer ends of the radial wires are connected between segments outlived its coaxial cable length of 2.5 m (used only braid). This increases the effective surface the resulting "virtual earth".
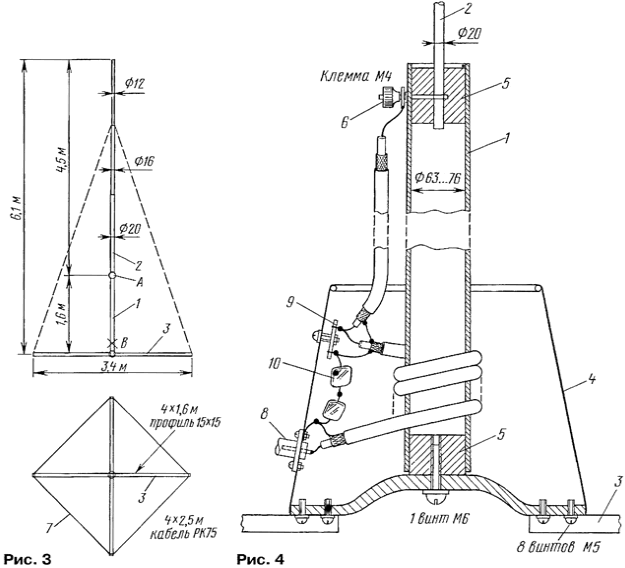
Since the antenna was designed as a dual band, it was decided to use one parallel circuit, which is tuned slightly higher frequency of 7 MHz. In the range of 40 meters it has inductive reactance and is lengthening coil, tuning the antenna to resonance. In the range of 20 meters contour has capacitive resistance and shortens the electrical length of the antenna, again tune it into resonance. The circuit parameters for a given size antenna optimized using the program MMANA, by placing the radials at a height of 0.2 m above a perfectly conducting ground (so we tried to take into account the effect of concrete roof the pavilion).
The simulation gave the frequency of the tuning circuit of 7.6 MHz inductance 1,24, CIC capacity 355 pF. From the Bay of the cable circuit with such a large capacity can not be done therefore, using conventional capacitors and cylindrical coil of cable, ensuring more efficient.
Design features manufactured GDP explains rice. 4. The circuit is placed in a cylindrical body 4 having a solid bottom, cast aluminum alloy, and relatively thin dural wall. The author used the tank pressed from old washing machine (for example, "Siberia"). Case dimensions are not critical (25 to 30 cm in diameter and in height). Present at the bottom of the hole does not close - they serve its intended purpose for plum accidentally caught rain water and of condensate.
To the bottom of the housing 4 screws attach the 3 radials. Particular strength in these the connection is not required, because the radials freely lie on the surface of the roof. The lower bearing element vertical antenna 1 is made of cut plastic plumbing pipe with a diameter of 2.5...3 inches. To secure the pipe 1 to the bottom of the housing 4 and attach the top of the radiating element 2 are cylindrical boss 5. Their can be made both from metal and dielectric material. At the top the boss is drilled radial hole through which the center conductor cable is connected to upper radiating element 2 to the terminal 6. She gives the mechanical strength of this node. Before tightening the clamps on the pipe 1 wear a lightweight plastic cover (Fig. 4 not shown), which accomplished holes for pipe and cable. Lid is lowered to the housing 4, protecting the circuit from precipitation.
The upper end of the cable must be equipped with a contact blade with a hole, suitable for terminal 6. The petal should be fixed strongly on external insulation cable, isolating it from the braid. With the petal connects the center conductor without its tension, which prevents the conductor from breakage during Assembly and disassembly GDP.
Four terminals are secured on the outer ends of the radial wires 3, and to the ends of the segments cable 7 "artificial land" pre-soldered contact lugs that significantly accelerates the Assembly of the antenna. The final strength to the whole structure attach four streamers of thin fishing lines shown by dashed lines on Fig. 3. Their tie to the element 2 in place of the upper articulation tubes and to the terminals at the ends of the radials.
Contour design clear from Fig. 4. On the side wall of the housing 4 is fixed coaxial connector 8 is preferably the same as in the radio (this will allow not to think within the antenna Assembly, which is the end of main feeder must go to the antenna, and which to the transceiver), and mounting plate with two blades 9. Yet one petal having contact with the housing 4, is fixed under the screw connector 8. To him solder the braided cable, which is wound on the coil, and one conclusion capacitor 10. The petals of the mounting plate 9 in contact with the housing 4 to have not needs. One of them solder the two center conductor and to the other braid of strands of the cable and the other lead of the capacitor 10. The capacitor is composed of, for reliability, two series-connected capacitors CSR working a voltage of 500 V with a capacity of 680 pF. It is permissible to use other high-voltage capacitors with a sufficient degree of sealing to to resist weathering.
Coil loop contains 7 turns of cable RK-75-4-11 wound closely on plastic pipe 1. Coil inductance adjust in two ways: either moving whole hog on the height of the pipe (closer to the bottom of the casing 4 decreases the inductance, increasing the frequency of the tuning circuit), or occasionally lifting the upper the coils, increasing the length of the winding generated by the gaps between the turns (the inductance also decreases). After setting up the coils fix insulation tape or twine covered.
The antenna tuning is simple. Collect it and install on the operating position (in case strong wind the ends of the radials 3 useful "weight" bags with sand or other improvised heavy objects), connect the antenna to the transceiver main cable. Removing the frequency dependence of VSWR in the range of 40 meters, determine where need to shift the frequency of the tuning circuit to the minimum SWR came in the middle range. For example, if the minimum SWR was below 7 MHz, the inductance of the coil need to reduce, and if higher at 7.1 MHz increase. Typically, you only need one a maximum of two adjustments.
Then check the SWR in the range of 20 meters. There the antenna is very broadband, and correction is generally not required. If such a need arose, it is necessary to change the ratio of L and C circuit and again to adjust the antenna 40 meter range. The increase of the inductance of the circuit while the reduction of the capacity lowers the tuning frequency of the antenna in the range of 40 metres and increases in the range of 20 meters, i.e., "pushes" the resonant frequency of the antenna. We after a single tuning of the antenna, which is installed on the reinforced concrete the roof, provided the SWR is close to unity in both bands.
During operation of the antenna I found that it also works well in the range of 15 meters, although there above the CWS. Automatic tuner of the IC-746 quite enough for her adjustment.
The concept of GDP opens up the possibility of constructing simple multiband vertical antennas. Even if the radio fan and will fail a good set of GDP, still he can be sure that the top, about five-meter, a part of the vertical antenna will radiate, and where we should be going in towards the horizon, and this is the key to successful results in DХ-Inge.
Literature
Author: Vladimir Polyakov (RA3AAE), Moscow






