The main purpose of the symmetric diacs - work triac in the power regulators. Interestingly the use of such a controller in the model scheme to enable the network adapter that is designed for a rated voltage of 120V, the network 220 (Fig. 1).
When using triac indicated on the diagram type and metal-film capacitor K73-17 rated voltage 63 In all elements of the regulator can be installed in the housing finalizing adapter A1. To configure the device to the output of the adapter should connect the required load and voltmeter, instead of the variable resistor R1 220 kω and permanent 51 ohms, connected in series. Reducing the resistance of the resistor R1, starting from the maximum value, set to the required load voltage and to replace the matched resistors on one as close as possible resistance.
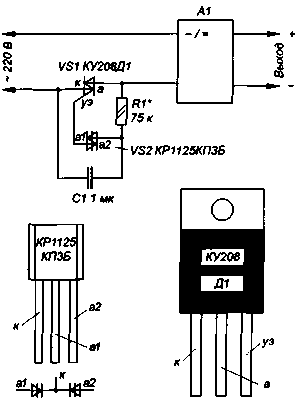
In the absence of the triac in a plastic case you can use regular - COV or COG. Capacitor C1 should be a metal film or paper. The use of ceramic capacitors is undesirable, since the temperature stability of the output voltage will be low. In Fig. 2 shows the dependence of the output voltage of the adapter Panasonic KX-A09 (120 V, 60 Hz), which are equipped with cordless phones KX-TC910-B, outflow load. Curve 1 corresponds to the supply to the primary winding voltage 105 At a frequency of 50 Hz, curve 2 - power supply 220 V 50 Hz in accordance with the circuit of Fig. 1 and the resistance value of the resistor R1, whereby the output voltage is equal to 11.8 In, and the load current of 120 mA. This point on the curve 1 was chosen for comparison of different options for enabling the adapter in [2].
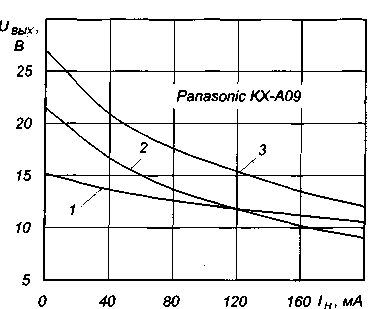
Curve 3 is removed by the resistance R1, providing a nameplate output voltage of the adapter 12 V and a load current of 200 mA. Curve 2 is close to curves 2 and 3 in [2], obtained for inclusion of the adapter to the network 220 through a resistor, but efficiency options include using triac controller much more, and the total dissipated power adapter - less. However, the output voltage ripple has increased slightly.
Interestingly, these devices are low voltage for powering appliances - dryers, electric shavers, etc. - produced by foreign manufacturers and sold in Russia. One of them, who came to the author, was called in translation into Russian: "Sputnik American tourist in France".
Perhaps the most interesting is the use of symmetric dynistor to stabilize the voltage transformerless power supply with damping capacitor. The scheme of such a device is shown in Fig. 3.
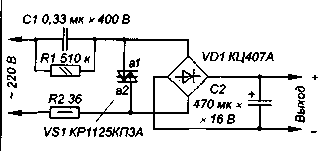
It works roughly as a block with a Zener diode, [3] but when charging the filter capacitor C2 to a voltage inclusion dynistor VS1 (up to a voltage drop on the rectifier bridge) it turns on and bypasses the input diode bridge. The load receives power from the capacitor C2. In the beginning of the next half cycle C2 is again charged to the same voltage, the process is repeated. It is easy to see that the initial discharge voltage of the capacitor C2 does not depend on the load current and voltage, therefore, the stability of the output voltage of the unit is very high. The voltage drop across the diacs in the on state is small, power dissipation, and hence the heating is much less than when you install a Zener diode.
The supply calculation symmetric diacs produced by the same formulas as for a source with Zener diode [3], but the minimum current through the stabilizing element ICT min would be either equal to zero, which somewhat reduces the required capacity of the quenching capacitor.
Experimentally has been verified by such source with the capacity of the capacitor C1 and 0.64 0,315 IFF (0.33 and 0.68 UF) and diacs KRKA and KRKS. The types and values of other elements correspond shown in Fig. 3. The voltage at the output of the block was about 6.8 and 13.5 for diacs KRKA and KRKS respectively. When supply voltage 205 V and the capacitance of the capacitor C1 =0,315 IFF the increase of the load current from 2 to 16 mA resulted in a decrease of the output voltage of 70 mV (i.e. the 1%) and 100 mV for 1=0,64 ICF and the current change from 4 to 32 mA. Further increase of the load current was accompanied by a sharp drop in output voltage, and the position of the point of fracture load characteristics with high accuracy consistent with the calculation in accordance with [3].
When you have to join one of the outputs of the source network wire [4] it is possible to apply the half-wave rectifier with damping capacitor (Fig. 4).
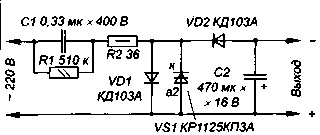
In this case, to reduce losses using only one of the diacs chip KRKS. Diode VD1 also serves to reduce losses and not mandatory, because diacs KRKS have a diode for passing current in the opposite direction. The presence or absence of such a diode in the diacs series CRK the documentation is not reflected, and buy a chip to the author for verification failed.
The maximum DC or pulsating current through the dinistor is determined dissipated them power and is about 60 mA. If to obtain the necessary output current of this value is not enough, you can "umonit" dinistor a triac (Fig. 5, (a) for use in the source according to the scheme of Fig. 3 or SCR (Fig. 5,6) for the device according to the scheme of Fig. 4.
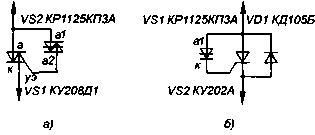
The advantages of power sources with diacs - lower power dissipation and higher stability of the output voltage, the disadvantage is the limited choice of the output voltage determined by the voltage inclusion of diacs.
Literature
1. Kuznetsov A. Triac power regulator with low interference. Radio, 1998, No. 6, pp. 60, 61.
2. Biryukov C. Connecting a small external 120 volt power supplies 220 V - Radio, 1998, vol. 7, pp. 49,54.
3. Biryukov, S. calculation of the utility power source capacitor with damping. Radio, 1997, No. 5, p. 48-50.
4. Biryukov, S. Thyristor power regulators. Radio, 1996, No. 1, pp. 44-46.
Author: S. Alekseev, Moscow; Publication: N. Bolshakov, rf.atnn.ru






