Sooner or later the radio there is a problem of making a universal power supply unit (PSU) that we could use "all occasions". That is, there was sufficient power, reliability and adjustable within wide limits the output voltage, also defended the load from "excessive consumption" current in the test and was not afraid of short circuits.
It is proposed, according to the author, the most satisfying these conditions is simple enough for the repetition of BP, providing a stable voltage of 1.5 to 24 V when the output current up to 3 A. in addition, it can function as a current source with the possibility of smooth adjustment of the current stabilization in the range of 10-100 mA or fixed values of current 0.1 A, 1 A, 3 A.
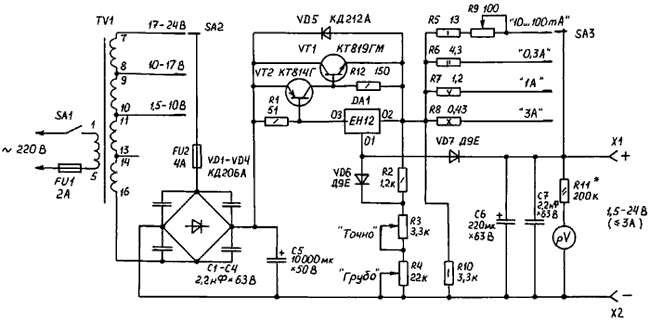
Fig. 1
Let's look at the power unit (see Fig. 1). It is founded on the traditional scheme of the voltage regulator, the "heart" - chip KREN, which is currently available to a wide range of radio Amateurs. As the power transformer is pretty powerful unified filament transformer TN-56, which has four secondary windings with the allowable current of 3.4 and a voltage of 6.3 V. each depending on the desired output voltage by the switch SA2 connect two, three or four series-connected windings. It is required to reduce power dissipated in the control element, and, therefore, increase the efficiency of the device and facilitate temperature. Indeed, in the most unfavorable mode, when the maximum difference between the input and output voltages (of course, if the output voltage corresponds to the range specified by the switch SA2) and the maximum current FOR the power dissipated on the control element of the power will be: Ppacc.max = (Uвx.max-2Uvd-Uвых.min)*Imax (1) Brass.max= (12,6-2*0,7-1,5)*3 = 29,1 W, where the Uвх.max - maximum input current voltage of a given range; Uвых.min - the minimum output voltage in this range; Uvd - the voltage drop across the diode rectifier bridge. It is easy to check that without the separation of the output voltage ranges power dissipation regulatory element power is 70 watts.
The AC voltage is rectified by a diode bridge VD1-VD4 and is smoothed by the capacitor C5. Fuse FU2 protects the transformer when the failure of the rectifier diodes. Transistors VT1, VT2 serve to increase the output current PSU and facilitate the operation mode of the integrated stabilizer DA1.
Resistor R1 sets the current through DA1, opening VT2:
IDA1 = Uбэvt2/R1 = 0,7/51 = 0,014 And, (2)
where Uбэvt2 - opening voltage emitter-base of transistor VT2.
At a current of 14 mA DA1 chip can operate without heat sink. To increase the stability of the output voltage of the regulating voltage is removed from the line of resistors R2-R4, is connected to the output circuit and is fed on "managing" the conclusion 01 DA1 through decoupling diode VD6. The output voltage regulation is performed by the resistors: R4 - "ROUGH" and R3 "EXACTLY". The current stabilizer is made on DA1, takasada resistors R5-R9 and the decoupling diode VD7. Select the desired discrete current stabilization is performed by the switch SA3. In addition, at the limit "10-100 mA" stepless current adjustment resistor R9.
If necessary, you can change the current stabilization by changing the values of sets of resistors using the formula:
R = 1,35/Stab, (3)
where R is the resistance dakotadome resistor, Ohm; Stab - current stabilization, A. Power dakotadome resistors is determined by the formula:
P = I*I*R, (4)
where I is the current stabilization range; R is the resistance of the resistor.
Real power dakotadome resistors from considerations of reliability deliberately increased. So the resistor R8 C5-16B selected power of 10 watts. In the constant current mode (switch SA3 in position "FOR") on the resistor dissipates power 3.8 W. And even if to put patially a resistor, its loading capacity is 72% of the maximum allowed. Similarly R7 C5-16B has a power of 5 watts, but you can also apply MLT-2. Resistor R6 type MLT-2, but you can put MLT-1. R9 - wire variable resistor type ARP-43 3-watt. R5 type MLT-1. These resistors must be placed so that they were cooled in the best way and not warmed possibly other circuit elements, as well as each other. For clarity adjustment (set current) at the limb of the resistor R9 doing at 10, 20, 50, 75 and 100 mA using an external meter (tester) by connecting it directly to the jacks BP.
For more convenience when working with BP provides voltmeter pV, which is used microammeter type M with the current total deviation of 0.15 mA.
The resistance of the resistor R11 is selected so that the final value of the scale corresponded to a voltage of 30 V. you can Also use any other process head with the current full deflection up to 1.5 mA, picking up a current limiting resistor R11.
As the switches SA2, SA3 are used disk - type NN. For increase allowable switched current is equivalent to the findings of the three wafers are connected in parallel. The retainer is mounted depending on the number of locations.
The capacitor C5 is prefabricated and consists of five parallel connected capacitors type K50-12 capacity 2000 UF x 50 in.
Transistor VT1 is installed at the outside of the radiator area of 400 cm2. You can replace CTA, CTA, VT2 can be replaced by CTG. A pair of transistors VT1, VT2 can be replaced by one CTA, B, C or D. the Diode VD6, VD7 any better germanium with a lower direct voltage drop and the reverse is not less than 30 V. the Diodes VD1-VD4 type KDA, KDA, B, C or similar installed on the radiators.
At independent manufacture of the transformer TV1 can be guided by the methodology described in [3]. An overall power transformer should be at least 100 watts, better 120W. You can demotte another winding voltage of 6.3 V. In this case, added another range of 24 - 30, which will provide load current 3 a range of output voltages from 1.5 to 30 V.
Adjustment of the power supply unit is conducted by a known technique and has no peculiar features. Correctly assembled BP begins to work immediately. When working with BP first switch SA2 select the range of output voltage, resistors "ROUGH" and "precise" exhibit the desired output voltage, focusing on the readings of the built-in voltmeter. Switch SA3 choose the limit current-limit and connect the load. It should be noted that given the simplicity of the scheme this power unit combines two devices: a voltage regulator plus the current stabilizer. BP is not afraid of short circuits and can even protect the elements connected to the electronic device, which is very important when carrying out various tests in Amateur practice.
Literature
1. Nefedov, A. V., A. I. Aksenov, circuit household radio equipment, circuits: the manual.-M: Telecommunication, 1993.
2. Akimov N. N., Resistors, capacitors, transformers, inductors, switching devices REA: a Handbook.-Minsk.: Belarus, 1994.
3. Semiconductor receiving and amplifying device: the radio Amateur's Handbook/R. M. Tereshchuk, K. M. Tereshchuk.-Kiev: Naukova Dumka, 1988.
Publication: www.cxem.net






