In the article, we recall the General principles of digital encoding of speech in telecommunication. The author quite prominently highly complex processes encoding used in digital cellular systems. Theoretical research and original engineering solutions to create an elegant small subscriber radiotelephone. About what is happening in complex processes, which users and even many professionals telecommunication't even guess the reader will learn from this article.
Riddles of speech signals has attracted the attention of researchers long before electrical connection. In the XVIII century one of the greatest mathematicians St. Petersburg academician Leonhard Euler (1707-1783) in a letter to a German Princess from June 16, 1761 wrote: "the Construction of a machine that was able to publish voices of our speeches with all the changes, it would be, without doubt, the most important the invention... the Addition of such a machine it seems to me not impossible."
The idea of the invention that talking car was worried minds of many artists, not only wanted to create it in the form as imagined by Euler, but as the means of transmitting speech at a distance. For example, the construction of such a machine did the inventor of the telephone Alexander G. bell (1847-1922). Ultimately, however, it turned out that the transmission of speech at a distance is possible without such machine. This was achieved quite simply. Using the microphone fluctuations air carrying the speech is converted to oscillations of electric current, passed down through the wires, and at the receiving end using the phone they once again transformed into vibrations in the air.
This method of transfer is called analog because of the obvious analogy between fluctuations in the air carrying the sound, and electrical oscillations transmitting the sound. Research analog speech transmission with amplitude modulation of showed that normal-quality reproduction of speech sufficient frequency band from 300 to 3400 Hz. This bandwidth was adopted as international standard, and built a worldwide network telephone connection. The principle of operation of this network now known not only to every Communicator, but and the General public.
Digital transmission of speech in wired communication networks
Fundamental changes in approaches to organization telephone if you have any translation of communication on digital technology. The advantages of digital methods transmission is widely known. Recall only the most important of these is the digital the technique allows to provide any given quality. For digital speech transmission is necessary to perform analog to digital conversion of speech signal is subjected to analog signal sampling, quantization, and coding. The combination of these operations is called pulse-code modulation (PCM). For accurate description of the shape of the speech signal, according to the Nyquist theorem, it the discretization have to spend with a frequency of 8 kHz (i.e. taking samples through every 125 μs), and to obtain normal quality reproduction of speech quantize each sample on a scale, divided into 8192 level (when selecting uniform quantization scale). To encode each value with reference using binary numbers, we will need 13 bits.
As a result, for transmission to the telephone conversation using the sequence binary pulses required speed h=104 kbit/s (which corresponds with optimal encoding of the band 52 kHz). Comparing this number with the band frequency 3100 Hz, which is required for analog transmission, not marvel at the tremendous growth the necessary bandwidth, which is necessary to pay for the advantages of digital transmission. Of course when you try the implementation of a digital transmission system to lower the transmission speed.
The first step in this direction is quite obvious. Quantization 213 levels is necessary because the levels of the analog speech signals can must be in the range of 60 dB. The high-level signals with a uniform the scale of quantization quantized with the same step as that of the low-level signals. But as the perception of bodies from the human ear is proportional to the logarithm signal level, then naturally it would be from the high level to quantize more roughly, a low level more accurately. Applying non-linear quantization with using the logarithmic law, you can do eight bits on the countdown is kept almost the same quality of transmission. As a result, the speed transmission of binary bits will be equal to 64 kbit/s. It is this speed received the most widespread, it is fixed in CCITT recommendation S. 711, and running equipment PCM in many countries.
Is it possible to reduce the speed further?
The analog signal has a greater redundancy. It allows you to predict once the countdown and transmit only the difference between the actual and predicted the value of each count. If you apply a good prediction scheme, change the amplitude of the increment signal is less than the variation of the amplitude of the signal, that will reduce the amount of transmitted information. On this principle based differential PCM (DICM) and adaptive differential PCM (ADIM), which allows you to lower the transmission speed of speech to 32 kbit/s and below, due to the further complicating transceiver equipment. Continuing to complicate equipment, it is possible to increase the transmission speed of speech to 100-300 bps. Can imagine, for example, on the transmitting side Converter speech-to-text, and on the receiving side - reading machine.
Known ways to further reduce the rate of transmission of speech, but not dwell on this to stop. The fact that the equipment of digital speech transmission at a speed of 64 kbps all satisfied because she turned out to be efficient at the most simple symmetrical cables twisted pair. Equipment PCM-30 began its triumphal procession with the seal of the connection lines between municipal telephone stations. Where before on cable pair could to arrange a connection line for transmitting only one conversation, instrument PCM-30 made it possible to organize for the same pair of transmission 30 conversations. About best the use of such a pair with analog multichannel communications equipment not could be considered.
Later, the instrument IKM-120 and other high performance systems, working on coaxial cables and optic fibers, and the issue is always about the decrease in the rate of transmission of conversational signals below 64 kbit/s networks wired connection was almost removed. Even numerous development equipment digital transmission at a speed of 32 kbps implemented in many countries based on the principle of ADIM (including development carried out in our the country under the direction of M. W. Pole), has not received sufficiently broad application. The balance between increased bandwidth channel forming equipment and complexity of terminal equipment in a wired connection yet tend to favor the first solution.
Speech encoding in a digital cellular radio communication systems
Very different perspectives opened in the late 1980's - early 1990-ies, when began to develop a cellular digital radio telephone. Unlike wired networks where capacity expansion is possible by lay new lines, i.e. the resumption of bandwidth resources, radio networks, there is a strict law of tightness in the air, and have to deal with non-renewable resource of radio frequencies. However, idea cellular and is the resumption of radio frequency resource by repeating the transmitting frequency on the territory, which does not reach the signal of the same frequency from interfering the radio station. But the possibilities of such a resumption of the resource is limited, therefore, a further complication of the apparatus for reducing transmission speed is justified.
For example, adopted in most countries of Europe the digital communication system of the cellular GSM standard transmission speed of speech are 13 and 6.5 kbit/s For the implementation of such a system transmission had to go to the old idea of a machine Euler and deeper penetration into the mechanism of speech formation.
As you know, one of the most important results of the modern theory of transmission information is the recommendation of the division of tasks of source coding and encoding channel. The task of encoding source information includes the description the transmitted messages in the most economical form, i.e. the removal of redundancy in the message. The thus obtained compressed message is more vulnerable to the effects of interference and may be distorted during transmission. Therefore, after the encoding of the source are applied channel coding, the task of which include protection of the message transmitted from interference. The channel coding required in the transmitted message some redundancy, but not random, that is present in the original message, and strictly justified theoretically, and which guarantees a specified transmission quality.
So far we have considered only the problem of source coding, which now, let's consider a more General view.
So, there is a digital version of the analog speech signal, i.e. the function describing, for example, the law of change of current with time. From this signal need try to remove redundancy. This problem can be solved in different ways. One of them is to try to find redundancy by purely mathematical analysis the considered function. Another way of solving the problem - acoustic analysis the characteristics of this function (from the point of view of its perception by the hearing). Finally, you can look for the redundancy of the modeling process itself the speech formation. It is the latter of these methods have found application in modern digital radio system.
The mechanism of formation of speech sounds is that rich harmonic sound the vocal cords of changing his strength and the fundamental frequency, is subjected to further processing in the oral cavity. The latter is, first, as the resonator, which, rearranging, highlights some frequency formants, determining the differences between the vowel sounds. Secondly, movement of the tongue, teeth and lips modulate the sound, producing different consonants. In the 1930-ies in Phone bell laboratories (USA) machine was built on the idea of Euler, principles of operation which was based on attempts to model the work of organs of human speech.
To synthesize speech at the receiving end of the communication system, the desired the acoustic frequency generator with a rich range, the white noise generator, a set formant filters (their number is low because the vowel sounds a little, and each of them are fairly well determined by two formants) and modulation scheme. With this set of equipment at the receiving end, you can pass on the communication channel voice signal, but only commands that control the synthesis process speech. Thus, a practical problem is to find a way generating the desired commands. It is this task is solved by the constructors cell phones.
In the GSM system the first releases of the original digital stream of speech signal with transmission speed 104 kbps split into separate blocks of 160 samples, are recorded. Each of these blocks takes a time interval of 20 MS (in other words, remember the sequence for h=2080 bits). Registered sequences are analyzed as a result for each of them there are eight filter coefficients, identify resonances and excitation signal. This the information is transmitted to the receiver, who plays her initial speech a signal such as occurs in the organs of speech (this body as configured using eight parameters, and then when the excitation it makes a sound).
But the analysis extends to relatively short segments time and cannot identify long vowel sounds, exciting neighboring blocks. Therefore, to eliminate the redundancy in the pronunciation of long vowels is applied the long-term prediction. To this end, in the transmitter remembered transferred sequences with a duration of 15 MS, which compares the current sequence. From already transmitted is selected sequence having the greatest correlation with the current (i.e. more similar to other current), and transmitted only difference between the current and the selected sequences. As recorded in the transmitter sequence known to the receiver, you need to pass only a pointer to how from the recorded sequences a comparison is made. Thus, we achieve a further reduction in the volume the transmitted information. As a result of this processing power is obtained the digital speech signal of a duration of 20 MS, containing 260 discharges and having the transmission rate of 13 kbit/s (i.e. eight times lower than the original). The described process is called regular pulse excitation with long-term prediction (English acronym PRE-LTR, which stands in the form of Regular Pulse Excitation - Long Term Prediction).
The next phase is in effect the encoding of the channel, which is protection from interference in the communication channel. Modern coding technique based on the deep ideas of algebra and probability theory. On the basis of these ideas developed a diverse and highly efficient coding methods are crucial in each case certain tasks. Will restrict ourselves here to a brief consideration of some of the ideas used in the GSM system.
Code protection can serve to either of discovery of the error, or to correct errors that have occurred. The first opportunity to carry out much easier and less benefit from it, because in this case you need to request retransmission of the message block in which an error was detected, or take into account the presence of errors. Because individual bits in a digital speech the signal obtained in the above procedures, the coding source, have unequal importance, they are divided into three subclasses and channel coding subjected to different methods of protection. Of the 260 bits of the received block most important are the digits that carry information about the filtering options on the amplitude of the signal block and the parameters of long-term predictions. These bits are so-called subclass Ia (50 bits). Then comes the subclass Ib (132 discharge containing pointers and information about the regular pulses of excitement, but also some of the parameters of long-term predictions). The rest 78 discharges are in class II.
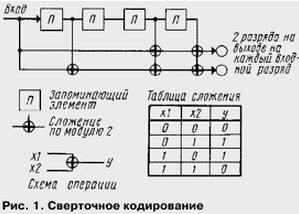
To protect these block are two ways of coding. First, used block code that is used to detect errors that remain uncorrected. This code belongs to the class of cyclic, in which each the code combination is obtained by a cyclic permutation of the elements. When encoding the code from the ranks of division Ia added three more test discharge for which the decoder can detect whether this subclass uncorrected errors. If the decoder detects the level of subclass Ia errors in transmission, the entire conversational frame of 260 bits reset. In this case the lost frame is reproduced by interpolation on the basis of information about the previous frame. It was found that with this solution the quality of transmission turns out to be better than in the case of erroneous bits of subclass Ia. Secondly, it applies a convolutional code, error-correcting. This name code due to the mathematical operation of convolution applied to the functions, describing the processing of the encoded sequence of bits. Unlike block code convolutional code is continuous in the sense that it the application of the processes of encoding and decoding are performed not over fixed blocks, and continuously going over the sequence of characters.
The convolutional code is applied both to the level of subclass Ia together with verification discharges and discharges of subclass Ib. These two sequences unite and increase by four digits (see below in Fig. 2) taking zero values. The latter serve to return the encoder to the initial state after performing the encoding. The applicable code is characterized by the parameters r=1/2 and K=5. The ratio r=1/2 shows that for each category, coming in at the input of the coder, coding sequence is obtained exactly two digits, and K=5 denotes the bond length, which is subject to the convolution operation. These characteristics can be understood by the scheme convolutional encoding, shown in Fig. 1, which shows a scheme of the addition modulo 2 (logical operation "exclusive OR"). Thus, the resulting encoding of the incoming 189 discharges obtained 378 bits, and added to these are unprotected level II class, resulting in a total block length is equal to the 456 bits (Fig. 2). This is exactly eight sub-blocks of 57 bits. From such sub-blocks are formed flash the radio time-division.
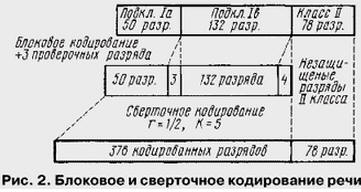
The present article is devoted to the coding of speech signals, and, as understanding can be described, at a fraction of the processor is placed in a small the handset, we have a fairly large amount of digital processing. However, this task processor is far from exhausted. As you know, is speech transmission system of cellular communication allows you to organize the transmission channel data that is encoded by different rules. But, in addition to logical transmission channels are useful (paid) information, cellular phone provides a large number of logical channels of transmission of control signals. To each of these logical channels have unique requirements information coding, and, accordingly, each such channel contributes its share in the load of the processor.
A General idea of the encoding schemes, as well as the formation of flashes for transfer all the logical channels in the radiotelephone system gives Fig. 3.
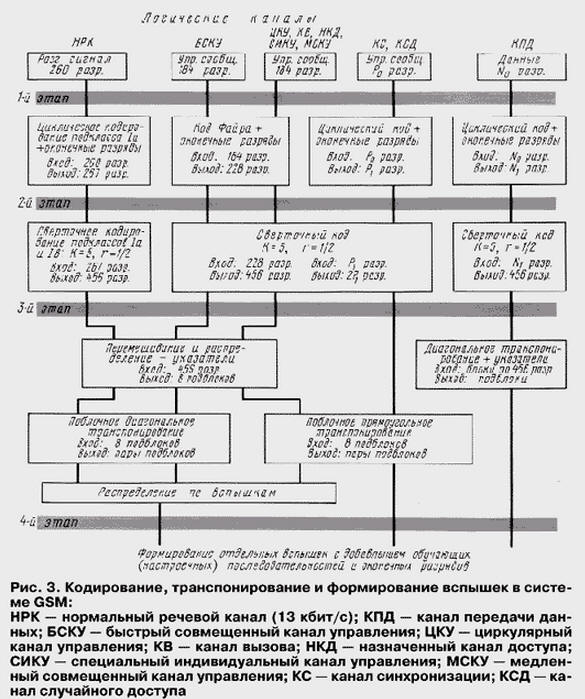
Here on the upper level shows the ten different logical channels showing the dimensions of the messages in these channels (in the form of specific numbers or alphabetic signs - P0 , N0, etc. - where these numbers can be changed). The following level shows the first stage of coding for different logical channels showing the number of bits of the original sequence and the sequence obtained after encoding. If the voice channel is applied cyclic code, detecting errors, then for the rest of the channels are different cyclic error-correcting codes, including cyclic code Fire, correcting errors. In the second phase encoding is applied mentioned convolutional code. Next (step 3) for distribution obtained 456 discharges for individual flashes (each bearing two blocks of 57 bits) operations are applied mixing bits and permutations of blocks (direct or diagonal transpose).
The total amount of signal processing in the cellular phone in the millions operations per second. Thus, unlike conventional phone cell phone is a tiny, but very high-performance computers. With the one hand, it analyzes "your" voice signal, producing a control commands for speech synthesis in the apparatus of the interlocutor, and this computer implements the idea of Euler, synthesizing the speech of the interlocutor on the control commands received from communication channel.
Author: V. Neumann, Professor, Dr. tech. of Sciences, Moscow






