The ignition voltage of the discharge between the anode and cathode of a thyratron type MTX-90, free when the grid is 150 to 320 V. But if apply voltage on the grid to excite the grid-current, the ignition voltage of the discharge can be significantly lower. Current grid 60 of the ICA, for example, you can lower the ignition voltage on the anode 50 to 80 V. This defines a rather high sensitivity of the photosensor, the scheme of which is shown in the figure.
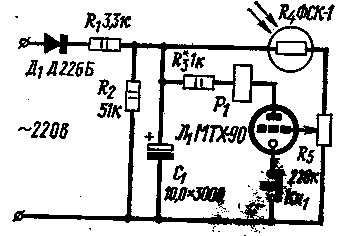
With divider R1R2 voltage, rectified by the diode D1, through the resistor R3 and the winding of the electromagnetic relay P1 is supplied to the anode of the thyratron. This same voltage is applied I to the food chain mesh consisting of a photoresistor FGC-1 and potentiometer R5. Capacitor C1 smooths the ripple of the supply voltage.
In the initial state, the voltage at the anode of the thyratron below the ignition voltage. The current in the anode circuit and no relay is not triggered. Under the illumination of the photoresistor the resistance sharply decreases, the current through the potentiometer R5 is increased, resulting in increased grid voltage until the voltage of the ignition of the discharge between the grid and the cathode. The thyratron is ignited and the relay P1 is triggered. The voltage at the anode of the thyratron is reduced, but remains above the voltage of burning. Therefore, the anchor confidently relay is held in the pulled condition.
Turns off the relay button KN.
Literature
Publication: N. Bolshakov, rf.atnn.ru






