Among the elastic vibrations of the air are of particular interest to long calls not perceived by the human ear ultrasound (from Latin ultra, next, more over), the lower limit frequency of which is considered to be 20 kHz. Insects, bats and even cetaceans have successfully used this natural the gift: some are for communication, some for hunting, others for the location of the area and bypass obstacles in poor visibility conditions. Peering into the role ultrasound in the animal world, man takes some of the identified "patents" nature itself adopted. In particular, uses a "silent" whistle. Hunter blows into it, and on this call, many completely inaudible, suddenly from the thicket you got a dog, who is capable of accepting consequently whistle commands.
No less popular and ultrasonic sounders, the analogs of which can be safely include "locators" cetaceans and bats. Sending this of the device, and then taking reflected from the bottom of the ultrasonic pulses captain the vessel receives operational information about the depths of the pond.
Is for ultrasound and other work. In chemistry, for example, it's getting fine emulsions in medicine - the study of the internal organs, metalldetektoren - detection of hidden cavities and cracks in the casting of parts. Fans of the popular science television programs, probably, remember shown Central television spectacular experience where standing peacefully Cup suddenly shatters into pieces, and explained: such destruction occurs at the coincidence frequency ultrasonic irradiation with a resonant frequency of fragile vessel and that provoked by ultrasound microexplosions promising to use to clean those or other surfaces.
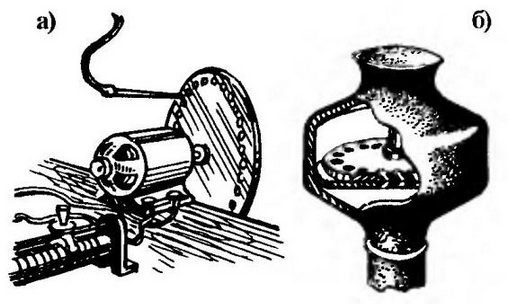
A method of producing the sounding of an air jet in the laboratory (a) and working on the same principle siren (b) as a source of fluctuations in the air frequencies multiple of the product of the number of holes the number of revolutions of the disk in second
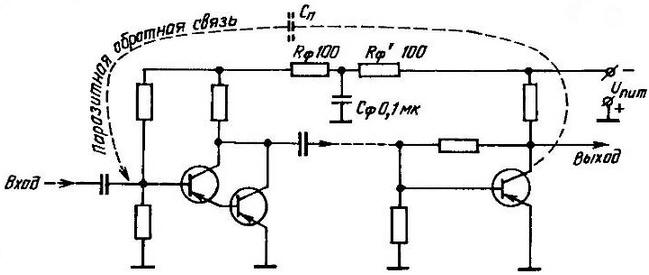
Filter for suppression of the excitation of the amplifier of electric signals on ultrasonic frequencies
Curious non-traditional method of obtaining ultrasound periodic interrupt a narrow stream of air rotating disk with a plurality of holes on circumference. When the jet is suppressed ascended the wall behind her is formed the vacuum was immediately filled with ambient air.
Range the arising vibrations of the air contains a lot of frequencies, multiple main (unit is Hz), which is determined by the product the number of holes in the disk at the rotation speed (Rev/sec). There here, of course, and ultrasound, which can be used for different purposes, including the control of harmful rodents (there is evidence that mice and rats, getting used to the monotonous ultrasonic vibrations, can not tolerate the periodic the frequency changes in the range of 25-50 kHz).
Here is an example of the negative influence of ultrasound. With him grapple with the operation of devices having electronic cascades with great odds gain, when it declares itself the so-called parasitic feedback input and output. The result is not only partially reproduced by the emitter ultrasound, from which humans start to hurt the ears, but hidden, not the perceived overload of electronic modules, threatening to release them down. Such undesirable effect of parasitic capacitance is neutralized by typing in General power circuit cascades special (for example, the resistance-condenser) filters RфСфRф.
Unsuccessfully be electronic methods and in the other, not only technical problems. For example, in the fight with the already mentioned rodents, using their specific reaction to the ultrasound. Readers - fans tinkering-it-yourselfers can recommend one of these protivorechivyh (protivokrazhnykh) structures: autoparallel ultrasonic emitter.
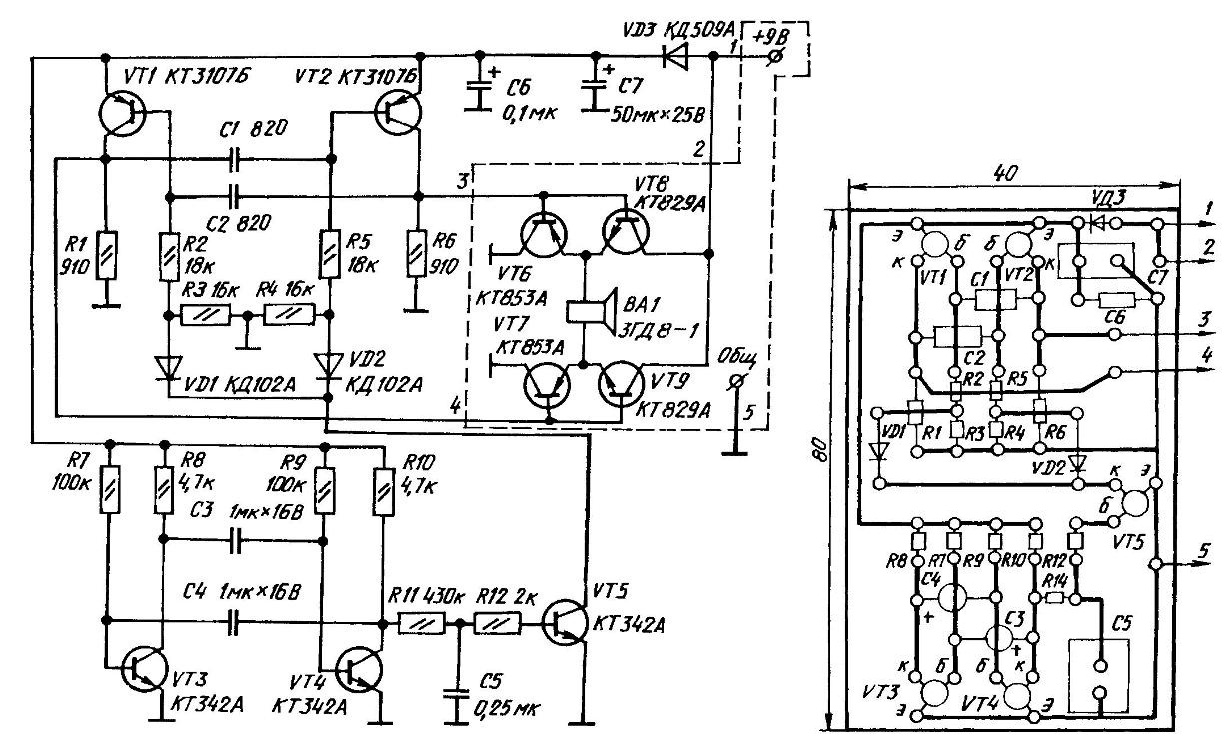
Schematic and circuit Board homemade an ultrasonic transducer "Antigreen"
Improvised device "Antigreen" contains two generators of electric oscillations, powerful output stage and an electrodynamic ultrasonic emitter hesitation, "swinging" the surrounding air environment. Base generator, working in ultrasonic field built on a symmetrical multivibrator transistors VT1-VT2. The corresponding switching frequency sets the values of the capacitors C1 and C2, and vapor resistance resistors R2 - R3 and R4-R5. In compliance with the values specified on the schematic the wiring diagram, it is approximately 25 kHz. However, if the resistors R3 and R4 short circuit, the frequency will be doubled. This and "deals" with regularity about seven times per second second generator, assembled on transistors VT3-VT4.
The UPS and downs of the voltage at the collector of VT4 control the transistor VT5, unlocking and locking it. An open transition collector-emitter of this semiconductor triode shunt (through the diodes VD1 and VD2) resistors R3 and R4, causing the frequency main generator increases. However, the switching of the transistor VT5 happen not abruptly, but gradually. Thanks to integrating the chain obtained R11С5 a kind of "walk" over the range from 25 to 50 kHz.
With the same frequency switch operates in the switching mode transistors VT6-VT9 output stage driven alternating pulses at the collectors VT1 and VT2. The high level of the load voltage VT1 unlocks the transistor VT9, and a low level at the output of the VT2 transistor VT6. As a result, the current from the source power flows in one half cycle of the generator BA1 through bottom-up, and in friend, when opened VT7 and VT8, in the opposite direction, causing dynamic head to work in unusual for her part the ultrasonic range.
Parts for the Assembly of such radiator is required the most common. In specifically, resistors MLT-0,25 and capacitors KLS (C1, C2), K73-11 (C5, C6), K50-20 (C7). As a radiator, an ideal "high-frequency" dynamic head type ЗГLW-1.
All parts of the device except power transistors VT6-VT9, mounted on pseudospectral (slotted) Board of one-sided foil fiberglass thickness 1.5-2 mm. Transistors VT6-VT9 used with radiators rectangular shape, which are mounted either on the circuit Board, or installed directly on the device, eliminating electrical connection radiators together.
A test launch of an ultrasonic transducer can be performed by nourishing it from six series-connected galvanic cells. In the normal mode the device runs continuously, so the power supply should be used with rectifier the filter is designed for a load current of 2.5-3 a at a voltage of 9 V.
Author: P. Yuryev






