If you are tired of constantly changing a blown bulb, use one the advice below. But in all cases, success is achieved through substantial voltage drop. In the daytime and especially at night the voltage in the network often reaches 230-240 V, which leads to accelerated fading of the filaments of light bulbs. It is estimated that the excess voltage only 4% compared to the nominal (i.e. from 220 to 228) shortens service bulbs at 40%, and with increased "power" of 6%, this period is reduced more than half.
At the same time reducing the voltage on the lamps only 8% (200-202) enhances the "experience" of their work in 3.5 times; 195 In it increases almost 5 times.
Of course, lower voltage is reduced and the brightness, but in many cases, in particular in offices and in public areas, it the circumstance is not so important.
How to reduce the voltage at the bulbs? There are two most simple method. First - consistently include two lamps (Fig. 1).
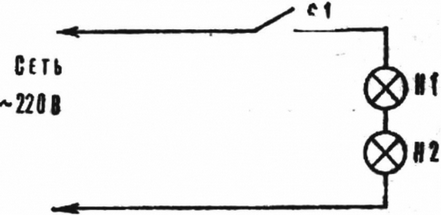
Fig. 1. Diagram of the serial connection of light bulbs
And what kind of lamp to take as an extra? Can be same as basic. But then both the lamp will illuminate poorly. It is best to pick a couple so that wattage differed by 1.5-2 times, for example 40 and 75 watts, 60 and 100 watts, etc. Then the lamp less power will glow brightly enough, the weaker and more powerful, fulfilling the role of a ballast, absorbing excess voltage (Fig. 2).

Fig. 2. Extra bulb
At first glance there is no winning - you have to use two lamps instead of just one. But here is the simplest calculation. The voltage drop across lamps in series is distributed inversely to their power. Therefore, when voltage is 220 V (will take a couple of lamps 40 and 75 watts) 40-watt lamp voltage will be about 145, and in its 75-watt "partner" - a little more than 75 V. as durability depends on the magnitude of the voltage it is clear that change will have mostly the smaller lamp power. And even that, as in practice, the worst case is at least a year. Under normal conditions for this time you have to change from 5 to 8 lamps (referring to the daily work within 12 hours). As you can see, the savings are very noticeable.
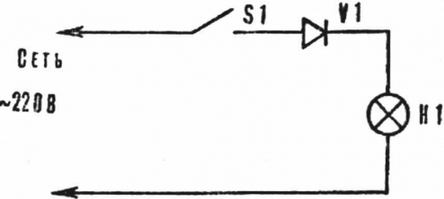
Fig. 3. Circuit of the diode
Another way is the series connection of lamps and semi-conductor diode. Due to its small dimensions it can be installed in the housing of the switch between terminal and one of the lead wires. In this embodiment, barely happens noticeable flickering lights (due to the half-wave rectifying AC current), and the average value of the voltage on them is about 155 V.
Now select the type of diode. It needs to have a certain amount allowable current and be rated for a voltage of below 400 V. Of miniature diodes this demand answer series CD and CD. However, the diodes of the brand should CD apply with lamps that have a capacity not exceeding 40 W, and the diodes CD (with any letter index) - to work with 75-watt lighting devices. Of course, you can use more powerful diodes of other types, but then you will need to set it outside of the switch. The correct diode is practically unlimited time.
But what if your house is the main switch for the whole staircase? In this case install one diode high power. It is attached to a metal corner, screw the screws to the wall around the switch and close the cover ventilation holes.
Recommended types of diodes: CDM, N, R or C, CD, D - D, D-D with any letter index.
When choosing the type of diode remember that its maximum permissible operating current (specified in the passport of a semiconductor device) by 20-25% exceed the total current consumption of all lamps at the same time relating to this the switch. For example, if the diode allows current to 5 A, the total current of all light bulbs (it is easy to calculate by dividing the total wattage of all lamps on mains voltage 220 V) must not exceed 4 A.
And last. By connecting an additional lamp or diode, do not forget that have working with high voltage, dangerous for your life. So be sure to unplug the line, and then get to work.
Author: Yu Rosenberg






