General principles for generation of oscillations
It is known that out of nothing nothing. To produce in nature any action, say, to create a movement, you have to spend some energy. Fluctuations, including electric, one of the movement types. The energy of the muscles needed to swing the swing, the energy of steam or water, accumulated behind the dam, to spin a turbine and generate electricity industrial frequency (50 Hz). Similarly, energy power source allows you to initiate a radio-frequency generator, which, in fact, is the energy Converter of direct current into the energy of high frequency oscillations - they can reinforce and bring to the antenna of a radio transmitter.
In the earliest radio transmitters, for example, the functions of generation and amplification oscillations were combined in a single device, is executed on a powerful radio tube (a even earlier on spark or arc the spark gap or high frequency). It later turned out better to generate oscillations are relatively small power (but stable), and then amplify them to the desired level. Generators, in which vibrations may occur independently, are called self-excited or self-excited oscillators, and power amplifiers, high frequency fluctuations are often called generators with external excitation.
Low-power generators - oscillators - are available in almost every radio and a television receiver. They are part of the frequency Converter - device used to transfer the signal from the received frequency so on called intermediate frequency, which occur main gain, filtering and signal processing. Such a receiver is called a superheterodyne.
The oscillator usually contains the amplifying element, the output of which is connected to the input of the feedback circuit, as shown in Fig. 44.
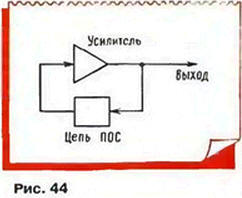
The polarity of the oscillations, input circuit for the operating system must be such as to maintain already available in the system fluctuations, increasing their amplitude Such an OS is called positive (POS). When the transmission ratio of the loop of the amplifying element is a chain OS more units only the slightest push, even thermal fluctuations in the oscillator having oscillation. Their amplitude will increase until, until not earn any deterrent mechanism that reduces the gain, for example, until a limit amplitude in the amplifier element.
Relaxation generators
If the generator is to apply a broadband amplifier and circuit OS (broadband - so skipping a broad band of frequencies, from very low to quite high), you get a relaxation oscillator. The process of self-excitation in it happens so fast, I don't have time to go through even one cycle (period) oscillation, as the amplifying element is in saturation mode (restrictions apply). After that, the device needs some time to "relax" (relax - relax) to return to its original state, then the process again.
Relaxation oscillators generate sinusoidal oscillations. Based on them create a generator of short pulses of rectangular, triangular, or any other voltage. They are used, for example, the generation of the voltage sweep in TVs. Inductors in the relaxation generators are most often not (the exception is the transformer in the blocking oscillator, and frequency or period of oscillation is determined by the duration charging-discharging of capacitors through resistors, i.e., the time constant RC-circuits (t = RC).
One of the easiest relaxation generators are usually done on the trigger Schmitt (Fig. 45,a) the device, the output voltage of which can take two values - high (say, 5 V) and low (O V). If the input voltage trigger increases, then at a certain value (for example, 3 V) output voltage becomes low, while when the input voltage drops below the other threshold (for example, 2 In) high. Thus, the transmission characteristic the Schmitt trigger has the form of a rectangular hysteresis loop, and to indicate that the figure on the callout. The fact that the output voltage inverted, i.e., has a reverse polarity relative to input, specifies the circle on the output pins. Ready Schmitt triggers are various series of digital circuits, commercially available.
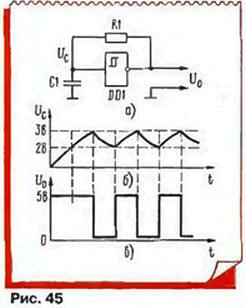
Running this generator is so. After switching it on, the capacitor C1 is discharged, the output voltage DD1 - high. Capacitor C1 starts charging through the resistor R1, and after a while the voltage across it reaches the upper threshold trigger (3 In). The output voltage is abruptly decreased to zero, and the capacitor starts discharging through the same resistor. When the voltage across it will drop to the lower switching threshold (2 In), the output voltage abruptly the age of g. This process will be repeated periodically - there will be self-oscillations. The shape of the voltage on the capacitor close to the triangle (Fig. 45,b), and the output of the generator is rectangular (Fig. 45,in).
Consider another widespread relaxation oscillator, done on discrete elements - multivibrator (Fig. 46).
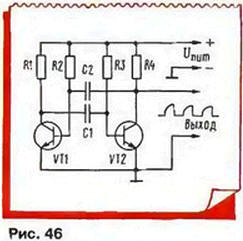
In fact this two-stage transistor amplifier with a connection between cascades through the coupling capacitor C1. A capacitor C2 connects the output of the amplifier with entrance, creating the OS. Because each stage inverts the signal, after two cascades the signal is non-inverted, and feedback - positive. R1 and R4 - resistors load the cascades, a, R2 and R3 resistors offset specifies an initial base current, providing saturation transistors.
The collectors of the transistors are formed antiphase pulses, on form close to rectangular. If the values of resistors and capacitors are the same, the pulses will be of the same duration - such a multivibrator is called symmetric. When different denominations parts impulses will become unbalanced - one half cycle shorter another longer. The multivibrator becomes asymmetric.
Schemes of relaxation generators a lot, they can be found in the electronic literature devoted to a pulse technique. Today, a similar the device in most cases performed on the digital chips that easier more convenient and safer.
Author: V. Polyakov, Moscow






