Renovating or developing automotive electronics, charging batteries are faced with the problem of stationary power these devices.
As described below, the power source is designed for just such purposes. He generates a load current up to 25 A, the output voltage is regulated smoothly in within 1.5...30 V.
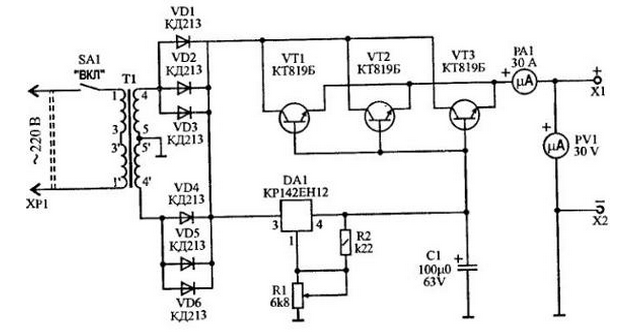
The source schema is quite simple. The voltage from the power transformer rectified full-wave rectifier diodes VD1 - VD6. Parallel the inclusion of diodes allowed to apply relatively affordable diodes KDZA.
The voltage output from the rectifier is fed to the integrated stabilizer DA1 - KP142EH12, the output of which, by means of the resistor R1 is adjusted permanent the voltage from 1.5 to 30 V. the Output current DA1 is not more than 1.5 And, therefore, on his the release includes powerful emitter follower connected in parallel on three powerful transistors VT1 - VT3.
The basis of the power transformer is taken from the old tube TS TV. This transformer is necessary to remove all of the secondary winding, leaving only network (labeled 1 to 3 and 1' - 3'). New secondary windings are wound wire sew-1 0.96 and contain 87 turns.
The housing is metal, on its side walls has two massive aluminum plates, which serve as heat sinks for transistors and diodes.
The plates are isolated from the body of mica and grease. In principle, it is possible housing use as a radiator, but in this case, you need to avoid contact him General disadvantage of the device, or from other power busbars or other buildings laboratory instruments or positioning the radiator plate over the entire area of the sidewalls, on a small distance from them, and in the sidewalls to drill lots of air the holes.
It is not excluded the application of the developed finned radiator together with electric fan from a personal computer.
Author: I. P. Shelestov






