In Fig. 6.16 shows the BP scheme, implemented on the available IC TDA4605. This chip has a domestic counterparts CEO, CREW.
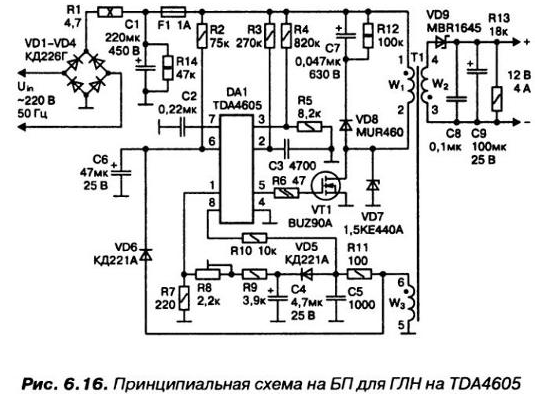
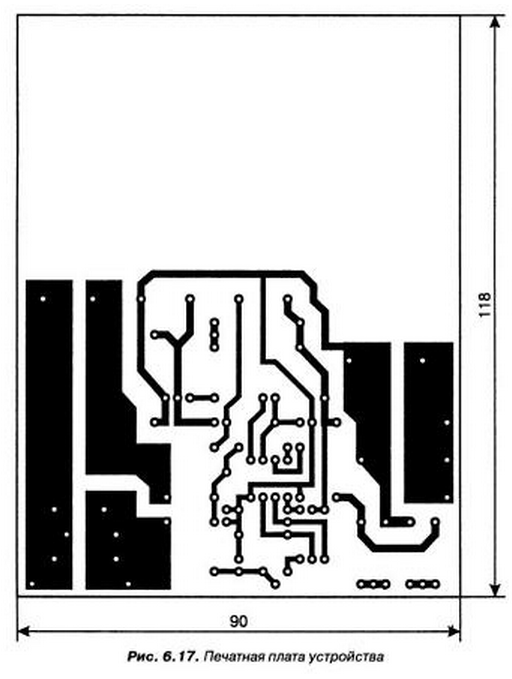
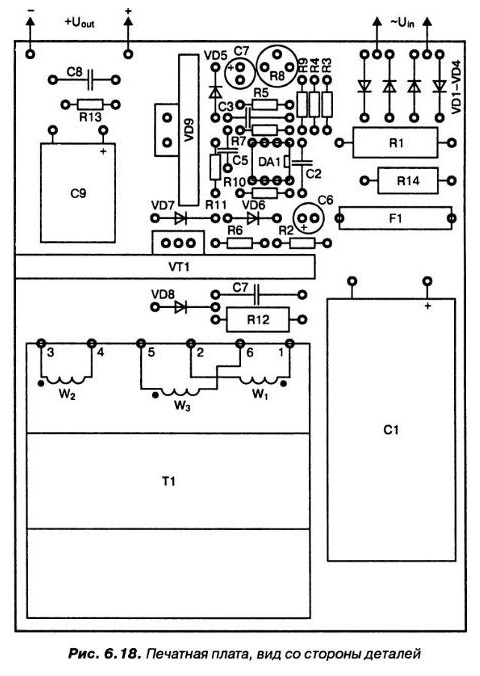
The transformer T1 is wound on a core. Sh ferrite NM Value non-magnetic gap of 0.12 mm (including double gap, i.e. two strips on 0.12 mm). The number of turns of the primary winding W1 = 64, the wire diameter of 0.25 mm. Number of turns of the secondary winding W2 = 3, wire diameter (bundle of five wires 0.6 mm). The number of turns of the feedback winding W3 = 3, the wire diameter of 0.25 mm.
Most electronic transformers have limitations not only on the maximum but the minimum total capacity of the connected lamps. It connected with the peculiarities of the internal converters. The range of valid capacities indicated in the catalogue and on the device, for example, 35...105 watts. This restriction, however, does not mean danger transformer output from building with no load (for example, when blown all lamps). It it is only necessary that the normal operation of the lamp power is less valid not guaranteed.
For ease of connecting lamps electronic transformers typically have multiple pairs of output terminals. The power regulation of lamps, depending on the specific circuit implementation, is done in one of two ways:
- inclusion of transformer with traditional dimmer;
- by feeding on its individual special control input signal (as in case with adjustable electronic ballasts).
This capability may not be provided at all. When connecting electronic transformer for dimmer traditional design is important make sure that the latter allows operation with capacitive loads of character. Such information is contained in the documentation on the dimmer.
It should be noted that the secondary voltage of their windings intentionally slightly reduced compared to the nominal, and usually is 11.2...11,6 V. This technique reduces the luminous flux and luminous efficiency of lamps, but prolongs their service life.






