Cordless telephone designed for connection to a conventional telephone line and to the power supply. In its composition includes base unit, which connects to line, and a portable phone handset with dialer. The connection between the base unit and telephone-handset cordless with two radio channels in the range of 64 to 73 and 88-108 MHz. The phone is not intended for use in field or road conditions, it has a small radius , and its purpose "detach" the caller from the telephone Jack and let him move with the tube in an apartment, small firms, or private house with not a very large area.
The range of ... 30-100 m.
The frequency of the transmitter of the base unit in the range ... 64 to 73 MHz.
The frequency of the receiver base unit in the range ... 88-708 MHz.
The frequency of the transmitter of the telephone handset ... 88-108MHz.
The frequency of the phone receiver tube ... 64 to 73 MHz.
The power of each transmitter is not more ... 10 mW.
The sensitivity of each of receivers when the ratio signal/noise ratio of at least 10 dB not worse ... 1 mV/m.
Frequency Manager signal... 2925 Hz,
The deviation of the frequency modulation, approximately... 50 kHz.
The voltage phone-tube... +9V.
The voltage of the base unit ... AC 220V.
The current consumption of the tube in release mode ... 8 mA.
Technical characteristics of the phone:
The basis of the portable unit is taken a simple phone handset Chinese production. All the parts connecting with the line removed, including combined spoken-pulse amplifier. Left lever switch, electrodynamic receiving the capsule , and the scheme dialer with chip, buttons, and power supply circuits. Printed fee phone-tube remains, with her only removed unnecessary elements,
A schematic diagram of a portable the block is shown in figure R. 01. It consists of three functional units (not counting dialer, which is already in the phone available): УSW FM radio on a chip A1, УSW FM transmitter transistors VT4, VT5, and the management node on the chip D1 and the transistor VT6.
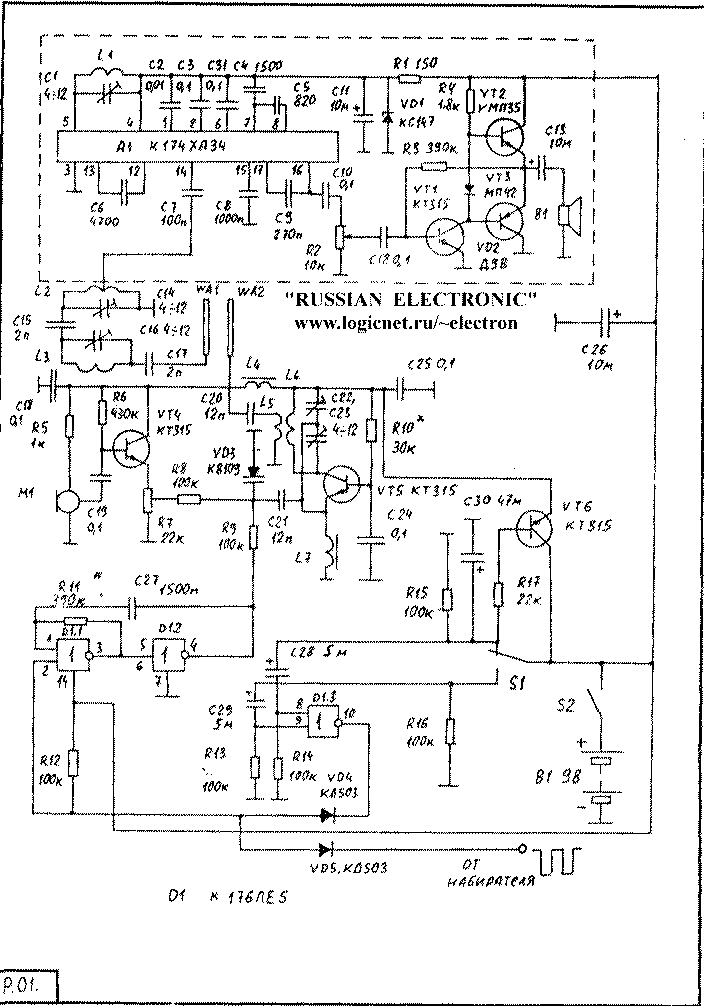
The radio is made on the chip CHA. The choice was made because this chip already beginning to appear on the market, and also has high sensitivity at low power supply voltage and a low current consumption. The second variant of the phone handset was made for the same scheme , but with the use of radio receivers tract from cheap pocket УSW FM radio Chinese or Indian production (just install failed, but it was clear that Japan and South Korea). Judging by throughout this tract was made on the chip, such KHA, because there was only one path and a minimum of hinged elements. In order transfer circuitry in the handset, wiring it the Board had to copy to the new card tube, and then carefully resoldering the chip and related elements. In other things can use almost any UKR FM tract with sufficient sensitivity and minimum dimensions, even on the basis UPCS-2, but in this case current consumption increases greatly. And not be sure that the base unit was the same tract as figurative.
The signal from the twisted antenna WA 1 flows through the filter tube L3 C16, who bars the way of the signal from transmitter input loop L2 C14. Then the signal is processed by chip A1 and the low-frequency signal with its output to using the volume control on R2 amplifier 3h transistors VT1-VT3. USC performed by a known two-stage scheme with push-pull output on germanium transistors The output USC included electrodynamic a primer from the phone handset.
The actual transmitter is designed for the transistor VT5 on single-stage scheme. Frequency carrier is determined by the setting circuit 16 C22 C23 C21 VD3. Modulation is performed the change in the capacitance of the varicap VD3, which is part of this circuit. For speech transmission is used electret microphone from the tape - the fact that the phone-tube was used as the microphone is the same the capsule, as and for the reception. In this case, it provided low quality and demanded additional amplifying stages.
The signal from the microphone is amplified the emitter follower at VT4. The varicap 3h is fed through a divider R7 and The R8.
Power to the transmitter is supplied through key cascade transistor VT6, which opens when lifting the handset. At this time switch S1 is set to shown in the diagram position. Thanks the capacitor C30, after the tube will assume power to the transmitter is supplied for few seconds, allowing him to pass the signal lights out.
To transmit information about the state lever switch tube (position - "off-hook" and "tube hung") and signals dialing, for almost the control pulse key base unit, use of a conventional single-channel system radio frequency coding, like the one that is used in the radio control systems models. The code signal frequency Hz 2925 is generated by the multivibrator elements D1.1 D1.2 . He starts by giving the zero level at pin 2 of the element D1.1. When it is necessary to transmit signals dialing, this conclusion receives a negative pulse from chip-phone dialer-tube. The length of signal transmission "off-hook" and "tube hanged." this conclusion comes longer pulses. Formed element D1.3. When hook the switch S2 is set to shown in the diagram position. Thus the capacitor C begins to charge through resistor R14 . over time charging of this capacitor, the output D1.3 there is a low logic level, and as a result all this time the multivibrator works. In order for the base unit switched to the state "off-hook" required pulse duration 1 sec.
As soon as the tube is lowered, the switch S1 is transferred to the opposite position, and now the same the pulse at the output of D1.3 is formed by time charging s through R13. S at this time discharged through R15
As a result, the scheme works as follows: as only you pick it up in the air is emitted the signal is modulated by a bundle of impulses, frequency 2925 Hz, which takes about 1 sec. Then you dial the number and the signal is modulated a sequence of shorter packets When you talk signal is modulated from 3H microphone, and when the tube is lowered, the signal again is modulated in a pack, with a duration of about 1 h
Special calling devices in the tube is no, the base unit generates the signal modulated frequency of 1000 Hz, which reproduced primer B1. At the same time and the base unit generates the signal built-in piezoelectric buzzer.
The details of the scheme on a drawing by R. 01 mounted on one printed circuit Board from sided glass the fiberglass. . The fee is the upper part of the tube, in the space between foster primer (B1) and the rear wall. RF tract the receiver is shielded brass "P" shaped plate, marked in Fig. R. 02 the dotted line, it has drilled holes trimmer capacitors
The upper end portion of the tube installed two twisted antenna. As frames are corps disposable pens with a diameter of 5-6 mm and a length of 100 mm, They are wound with wire sew 0.5 in 15 turns with a pitch of 6 mm. Then they stretch soft PVC pipe black. The distance between the antennas is 40 mm.
In the proposed design used the following details. All permanent resistors - MLT 0,125, variable resistor volume type SPZ-3 with switch and end handle (used as volume controls pocket receivers). The trimmer-Spa. Trimmer capacitors ceramic PDA, constant KG, KD, KM, K10-7, electrolytic K53-14 Zener X can be replaced by COP'133, instead of the varicap can also use a Zener diode to a voltage exceeding 8 9 (for example DD-1). Chip CLE can be replaced by CLE. Transistors with any alphabetic indices, Microphone MKE-3, or another with built-in amplifier.
Coils L1, L2, L3. L5, L6 frameless. They are wound on the mandrel with a diameter of 3 mm, which are then removed, L1 contains 13 turns L2 - L3 turns taped from the 3rd, L3 contains 7 turns. For winding wire is used sew 0,35 L6 - 5 turns. L5 - 2 turns of wire sew 0,35. Inductors L7 and L4 wound on the permanent resistors MLT 0.125, and contain 60 turns of wire sew 0,12.
When mounting the tube pin 1 of the chip dialer need to connect via series-connected diode and resistor CD 10 kOhms with a connection point R15 and R17 and pin 17 through a resistor 47 ohms with a connection point R16 C29 General the wire you need to connect together pins 2, 6, 10, 11. Pulse signal to remove from the 18th output (data for the chip KS5805A).
Setting a receiving tract need start with the voltage at the emitters VT2 VT3, which is half of the voltage power, the selection of R3. Then you need unsolder C7 and solder a piece of wire with a length of 10-15 cm conclusion 14 A1. and try to tune in on one out of radio range of 64 to 73 Mcwra rotor C1. Now you need to atlatl wire and solder C7, and then to configure the circuit C14 L2 so that to ensure reliable reception of the radio station
Configuring the transmitter is reduced to setting the carrier frequency in the area range 88-108 MHz, which in the area no radios , which can be determined by exemplary receiver. And set to maximum transmission distance (also for exemplary the receiver). Perform this setting consistent tuning capacitors C22 and C23. Podstroechnik set R7 for the best sound for speech , spoken in front of a microphone, listening to it through an exemplary receiver.
Now we need to configure the filter-tube L3 C16 minimum penetration of the signal from transmitter to the receiver input,
Configuring the management node is reduced to setting the frequency at the output of the multivibrator 2925 Hz (not necessarily exactly) the selection of R11. And selection R13 and R14 so that when you switch S1 multivibrator formed a pack lasting 1 second.
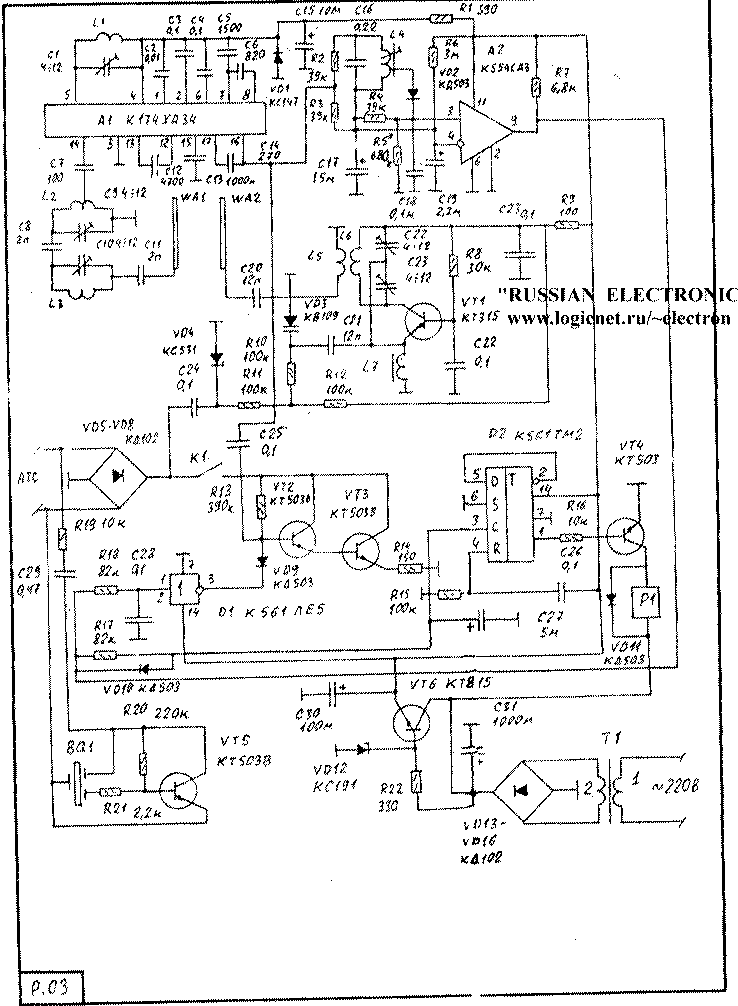
Schematic diagram of the base unit shown in figure R. 03-Receiving tract made in the same way as in phone-tube, with the difference that the tract tuned to the frequency range 88-108 MHz, and output OSC replaced by a resonant comparator on the chip A2 and loop L4 SB. As already noted, the scheme is based on the following scheme radio frequency-temporary division of channels. This means that when you set rooms or when removing or lowering the tube the transmitter of the telephone handset emits in the air frequency modelirovanie impulse frequency modulation which 2925 Hz, and the duration depends from the transmitted commands (dialing or "the position of the tube"). Contour L4 configured to C16 this frequency. At a time when the input signal missing the inputs of the comparator goes the DC component of the output of the detector through resistors R2, R3, R4. At the same time on inverting input receives an additional the bias voltage through a resistor R6. As a result inverting input the voltage is slightly bigger and the output of the comparator is set to zero When the signal with the frequency loop L4 C16, on the cathode of the diode VD2 you receive a positive voltage. In the result, the voltage at the direct input is higher than the inversion and the output the comparator switches to one state. The duration of this state depends on duration frequency modulated pulse, emitted by the transmitter tube.
From the output of the positive comparator the pulse is fed to two ramasadaya chain R18 s and R17 S. If goes a long pulse, the capacitor C time charged to a single level and the pulse is fed to the input of flip-flop D2. As a result, the trigger takes the opposite set state and translates (using electromagnetic turnips P1, which replaces lever switch) line in condition of employment or hang up. Source state at power - state lights out, the contacts K1 in the open position When turn on to a busy state (off the hook) the contacts K1 are closed and connects to the line spoken-pulse cascade transistors VT2.VT3.
When dialing duration pulses are much smaller and cannot charge S time, therefore, the state of the trigger remains unchanged. Short pulses arrive at the input D1, diode VD9 reduces the bias voltage on the base transistor VT2, translating the whole cascade into a state with a small collector current- Pulses of collector voltage perceived line of work as dialer.
After entering the phone number at the output D1 set your unit, and spoken-pulse cascade enters a state with a high current. It now collector current is changed in accordance with speech signals coming from the output detector A1 to its input through a capacitor C25.
To listen to the ringing signal, conversational signals from line serves as the transmitter transistor VT1, which is made by the same scheme as in the tube, but it works in the range of 64 to 73 MHz. Its RF the signal is modulated using a varicap VD3 . Signals 3H him come through capacitor C24, VD4 is used to limit the amplitude of these signals.
Call the signal emitted by the tube soft, so use advanced calling device on the transistor VT5 and photoelement BQ 1.
To power the scheme is used source 9V consisting of the transformer T1 and rectifier on VD13-VD16 with stabilizer on VT6
The details of the circuit in figure P 03 mounted on the same Board of unilateral foiled fiberglass, drawing Board and the wiring diagram are shown in figures 04 and R. R. 05. Charges come in a plastic case dimensions HH mm, there is power a transformer. The RF receiver path is escaped brass "P" shaped plate, it drilled hole trimmer the capacitors . On two opposite sides hull are two folding telescopic antenna with swivel hinges (compact radios).
And designs are used to make permanent resistors YGT of 0.125. Trimmer capacitors PDA, constant KD, KT, K10-7, electrolytic C50-14 or C50-35. The Zener diode VD1 can be replaced on X, VD12 on DD-1, VD4 on any voltage 12-31V, or a chain of Zener diodes, for example two serially - DD.If the varicap replace the Zener diode, VD4 should be, for a voltage not more voltage stabilization the Zener diode is a voltage variable capacitor. The chip can C replace with similar K. Electromagnetic relay 12V - RES 22, such relays are completed kits for self-Assembly TV remote control (for the power switch) you Can use another relay for 10-12 V. and a current of 60 mA System from the phone handset.
Coils L1, L2, L3, L5. L6 frameless, have the same design as in "the tube". L1 contains 7 turns, L2 - 7 with tapping from the 2nd, L3 - 13 of turns, L6-10 turns L5 - 3 turns of the Inductor L7 is wound at a constant resistor MPT 0,125 the resistance greater than 10 ohms, contains 60 turns sew 0,12. Coil L4 are wound on the frame from the inverter circuit of the receiver "VEF 202 with trimmer and armoured core cups (you can use the SB-23A with podstroechnik). The coil contains 270 turns sew-0,12.
For transformer used core sh-h Primary winding contains 4400 turns sew 0,09, secondary - 230 turns Sew 0,23. You can use any ready a transformer with an output AC voltage 8-12V and power of 10W.
Setting the base unit need carried out in conjunction with the "tube" held the preliminary setup. Transmitting speech the signal from the handset needs to be set to the frequency transmitter tube circuit with the coils L1 and L2 Control signal when the test USC, on which input to signal CC from the output 16 of the A1 (via the capacitor). Then you need to unsolder the cathode of the diode VD5 (Fig. R. 01) from microchip dialer and connect it with the General wire. Now you need to control oscilloscope level at pin 9 A2 (Fig P 03) tuning L4 (B. 03) and selection resistor R11 (B. 01) to set a position at which at the connection of the cathode VD5 (Fig. R. 01) common wire to pin 9 A2 (Fig. R. 03) set your unit. Now we need to reconnect VD5 (B. 01) and install the sensitivity of the comparator A2 (B. 03) the selection R5 so that he confidently worked at admission pulses and typesetting didn't work during a call. Now we need to find the value R17 thus, to the level at pin 1 D2 (B. 03) changed by clicking on the button lever switch phone-tube and did not change with dialling.
Configuring spoken-key node on VT2 and VT3 (B. 03) comes down to setting the voltage at the collectors these transistors 7-10B in the absence of a signal from tube and closed contacts K1, selection R13.
The transmitter is set up as the transmitter tube. Using a model the receiver selects the point on the scale range of 64 to 73 MHz, where there is no radio station , and adjust the capacitors C22 and C23 transmitter in this place range. For ease of configuration makes sense on the capacitor C24 to signal from Gzch C, first disable the device from the telephone line. Then you set up the receiver tubing on the frequency of the transmitter of the base unit adjusting C1 and C14 (B. 01).
Now stay tuned circuit L3 C10 (R-03) by the maximum suppression the signal from the transmitter (B. 03)
Author: Pavlov S. I.; Publication: N. Bolshakov, rf.atnn.ru






