Whether you love the TV so as not love him I?
The TV is actually ugly thing. Than to sit for hours in front of a "blue screen", it is much more beneficial to lead a healthy lifestyle: slowly, with a Cup of coffee at the computer...
However, the things that I write in this series might well be useful in our practical activity.
So, now we will look at how the transfer occurs video. To consider we'll be native to the pain SECAM system, because in our country ( Russian Federation) officially adopted it is this system of television. However - everything in order.
How does the TV work?
The TV is on 24 hours a day, 7 days a week. It clear.
He has a screen and speaker 1pc - from 1 to infinity, depending on the "advanced" unit. He has a antenna and remote management. But right now we are only interested in the screen. And let us Housewives on the tongue of the wise cats - CRT (cathode ray tube - CRT).
I understand that in this age of plasma and liquid crystal, electron-beam kinescope think someone is a relic of antiquity. However, to understand the principle of operation of the TV, it is easier dealing with CRT.
A cathode-ray tube
Sho chain take. Where are the electrons? Where are the rays?
The fact that the picture is drawn using of the electron beam. The electron beam is very similar to light. But light the beam consists of photons and of electrons, and we can't see can. A bunch of electrons travelling at breakneck speed in a straight line from point A - to the point B. this forms a "beam".
Point B is the anode. It is located directly on the reverse side screen. Also, the screen (reverse side) smeared with a special substance - the phosphor. In the collision of an electron at breakneck speed with the phosphor the latter emits visible light. The faster electrons to flew collision - the light will be brighter. That is, the phosphor is Converter "light" of the electron beam in the light, visible for of the human eye.
With paragraph B sorted out. What is the point "A"? And is the "electron gun". The name is terrible. But anything terrible no. It is not intended to brutally shoot the aliens from Mars. But "shoot" it still knows how - electron beam at the screen.
How does this work?
Generally, a CRT is a large vacuum tube. How? You don't know what is lamp? Well...
The electron tube is amplifying the same elements like and beloved transistors. But the lamp appeared much before their silicon counterparts, in the first half of the last century.
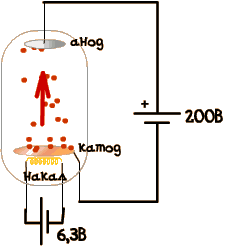
The lamp is such a glass bulb, from which air is pumped out.
In the simplest lamp - 4 output: cathode, anode and two withdrawal of the filament. The filament is needed to heat the cathode. And preheat the cathode need to with his flying electrons. And electrons must fly then, that there was an electrical current through lamp. This is typically done on the filament voltage is 6.3 or 12.6 In (depending on the bulb type)
In addition to flew electrons have high the voltage between the cathode and anode. It depends on the distance between the electrodes and the lamp power. In conventional tubes of this tension is a few hundred volts, the distance from the cathode to the anode in such the lamps do not exceed several millimeters.
In CRT, the distance from the cathode in an electron gun to the screen may exceed a few tens of centimeters. Respectively, and the voltage they need much more: 15...30 kV.
Such atrocious voltage creates a special increase transformer. It is also called a flyback transformer, because it operates at lower frequency. But, more about that later.
When the stress of the electron on the screen, in addition to visible light, "knocked out" and also other radiation. In particular radioactive. Here why it is not recommended to watch TV closer 1...2 meters from the screen.
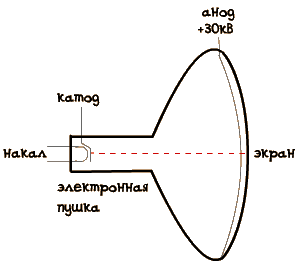
So, the beam is received. And he's so pretty shining right in the center of the screen. But we need it to "draw" across the screen lines. That is, need to get him to deviate from the center. And this mom will help... the electromagnets. The fact that the electron beam, unlike light, very sensitive to the magnetic field. Therefore, it is used in CRT.
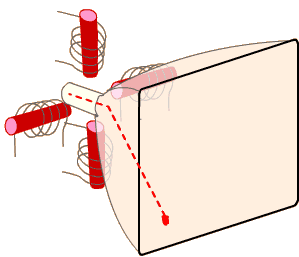
You need to put two bunks deflecting coils. One pair will reject horizontally, the other vertically. Skillfully manipulating them, it is possible to drive the beam on the screen anywhere.
And wherever you go?
From here we begin our tale of the points and lines the hooks...
The story of Lines, Points and Hooks
The picture on the TV screen is formed by that beam with breakneck speed draws a left-to-right top-to-bottom across the screen. Like this the method of successive drawing of the image is called "scan".

As the scan is very fast for the eye dots merge into lines and lines into a unified frame.
In PAL and SECAM for one second beam time to run an entire screen 50 times.
In the American system NTSC - more - as many as 60 times! Generally speaking, PAL and SECAM differ only in the transmission color. The rest of them - equally.
The picture is formed due to the fact that during the "run", beam changes its brightness in accordance with the received video signal. As controls the brightness?
It's very simple! The fact that in addition to considered electrodes - the anode and the cathode, the lamp is still the third electrode grid. The grid is a control electrode. feeding on the relatively low net the voltage, you can control the current flowing through the lamp. In other words, you can control the intensity of electron flow, "flying" from the cathode to the anode.
In the CRT grid is used to change the brightness of the beam.
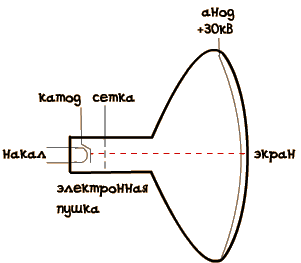
Feeding on the grid a negative voltage (relative to cathode), it is possible to weaken the intensity of the flow of electrons in the beam, or even close "the road" for electrons. This is useful, for example, when the beam from the end of one line to the beginning of another.
Now let's talk more in detail about the principles sweep.
For starters, remember some simple numbers and terms:
Raster is a single "line", which draws the beam on screen.
Field is all the lines that drew the beam in one the vertical passage.
The frame is the basic unit of the video. Each frame consists of two fields: odd and even.
It is worth to clarify: the image on the TV screen takes place with a frequency of 50 fields per second. However, television standard is 25 frames per second. Therefore, one frame in the transmission is divided into two fields: odd and even. In the even field contains only the even lines of the frame (2,4,6,8...), in the odd - odd only. The image on the screen is also "drawn" through the line. Such a net is called "interlaced scan".

There can be a "progressive scan" - when the whole the frame is deployed in one vertical stroke of the beam. It is used in the computer monitors.
So, now dry. All the numbers fair for PAL and SECAM.
Number of fields in a second - 50
Number of rows in the frame - 625
The number of effective lines per frame - 576
The number effective pixels per line 720
And these numbers are derived from the above:
Number of rows in the field - 312,5
Line frequency is 15625 Hz
The duration of one line is 64 μs (with reverse swing beam)

Next, we'll talk about the parameters of the video and draw scheme for synthesizing synchronization pulses.
Publication: www.radiokot.ru, www.cxem.net






