Modern electric kettles automatically disconnects when them water begins to boil. This service can be administered in the usual kettle, if to complement his simple device, which is described in this article.
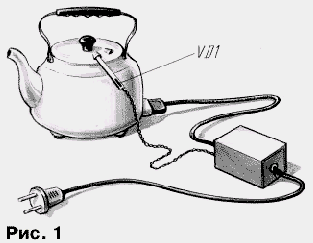
As a sensor of boiling water is a simple device (Fig. 1), consisting of a flexible tube and a thermosensitive element, placed inside it with one hand. The other side is a tube inserted into the hole in the lid of the kettle so that the heated air and steam got into it. At the moment boiling water increases the flow inside the tube that is fixed the temperature probe.
As the thermosensitive element used germanium diode VD1 (Fig. 2) with its strong dependence of the reverse current from the heating temperature. When cold body diode reverse current is small and the trigger is assembled transistors VT1 - VT3, is in the original condition in which the transistor VT1 is closed, a VT2 and VT3 open. Open state of the transistor VT3 causes unlocking triac VS1, resulting in the heating element of the kettle is connected to network. When the water boils, the temperature inside the tube is increased, which leads to the increase in reverse current diode VD1, as a result, the VT1 transistor opens and the trigger enters the opposite state of the transistor VT1 is open, a VT2 and VT3 is closed. This leads to the locking of the triac VS1 and disconnect the kettle from network.
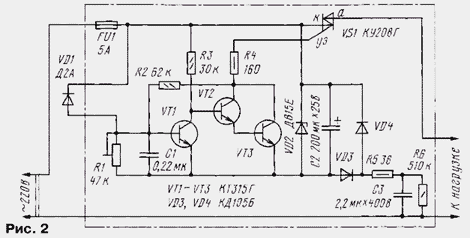
To re-enable, you must turn the device off for 5...10 s and again to turn it on. Capacitor C1 suppresses possible interferences in the sensor circuit temperature and ensures proper installation of the trigger when you turn on power.
The sensor is made of flexible thick-walled tube of insulating material, it has a length of 120...150 mm and inner diameter 6...8 mm. One side of the tube inserted into the slightly enlarged hole in the lid of the kettle that is designed to the steam outlet. The VD1 diode with pre-soldered wires for sealing dipped in epoxy resin and, after curing, is fixed inside the tube at a distance of 15 to 20 mm from its opposite side (for example, glued to the wall). The conductors coming from the diode, it is desirable to twist. The diameter of the tube needs to allow free passage of steam through the tube when in the diode. Other variants of installation of the sensor, however you must make sure that he fired only when full of boiling water (control change in reverse current diode).
Diode VD1 should be germanium, for example, from the series or D2 D9 with any letter index. Allowable power applied load is determined by the triac VS1 - for the device driven by the scheme in case of installation of the triac on the radiator it is 1100 watts. If necessary, you can use a more powerful triac, this may have to pick up the resistor R4 in accordance with a control current of the triac, and also replace the transistor VT3 to more powerful. Resistors and the capacitors can be of any type.
The device is assembled in a small body of insulating material. When regulation should, gently moving the slider to the resistor R1 from the lowermost (the scheme) provisions to achieve the switch on the load. After that the engine is a little resistor is moved in the opposite direction. It is also advisable to check the current through the Zener diode VD2, which is open when the transistor VT3 needs to be 25...35 mA. Finally, the threshold is adjusted according to the time turn off the load when the water boils.
The water level during operation must ensure that the overlap of the holes, connecting the primary reservoir of the kettle with a spout.
It must be remembered that all the elements of the device are under voltage, therefore, the circuit elements of the sensor and the device as a whole must have reliable insulation. You also need to observe safety when creating a device.
Author: Zaitsev, St. Petersburg






