The rapid development of new telecommunications technologies in 80 - 90th years connected with the active use of science and technology in the industries telecommunication, information technology and electronics. One of the priority technology is cellular, which is gaining popularity the population and is growing very rapidly.
"Don't turn away from a possible future, unless you are absolutely sure that there is nothing what you could learn."
Richard Bach "Illusions"
World championship
Like those readers who prefer to view the log from the end, you get a jump too far ahead and say the main thing: today there is no such kind of telecommunications, which have developed so fast as wireless radiotelephone, and especially cellular serving mobile users. The number of such users increasing annually by about 40 % and recently stepped 350 millionth milestone. It should be noted that individual cell types mobile networks show an even more impressive growth rates. In the world the annual growth of subscribers of GSM to about 70 % (http://www.gsmworld.com), and cdmaOne networks, known here as CDMA/IS-95, for the last year he has reached almost 160 % (http://www.cdg.org)! It is expected that the number of cellular subscribers will reach 1 billion sometime in 2002-2003.
Although from the moment when the cellular network emerged from the stage of scientific and technical developments the commercial market (the turn of the 70-80-ies), was not so much time cell phone now ceased to be a symbol of prestige and became a tool allowing more efficient use of working time, operational control technological, economic and other processes. Mobile network not only grow in breadth, but steadily increasing the number of available advanced services.
If we take the density of cellular networks, which reached many developed countries (data from British Telecom Engineering), the undisputed leader among them is Finland, where about 70% of the population have cell phones. A little behind her neighbors in Scandinavia (50 to 60 %), between which is interposed a piece of China (ex Hong Kong). Another six countries, including Australia and Japan, stepped 30% abroad, but a group of countries, including the UK and the US, closely it approached. About 20% of the indicators are Germany, France, Spain, Canada and several other countries. However, you can still a long list of successes mobile and given enough information to make some conclusions.
All of the above suggests that in most of these countries the density radiotelephone lines has already reached the level density of the lines of traditional telephony (about 50 - 60 %) or was it at least half. Many of these countries have either very large or very numerous the population, or both simultaneously. So even 5 % in Brazil and 3 % in China excluding Hong Kong (what a petite figure and at the same time monstrously large the number of users) are more significant than, for example, 27% somewhere in Holland. In General, mobile communication has become a product of mass consumption and continuing to increase the growth rate.
Impress even the closest predictions (2003): in terms of population coverage a group of countries would come close to 90 %. and the former Hong Kong (now special administrative region of the PRC) will be the first area, where the rate will reach 95 %! Nearly two dozen countries in terms of density will be in the range of 60 to 95 %. However, even highly developed countries with relatively large areas will not move so far: USA - 53 %, Germany - 47 %, Canada - 30 %, Brazil - 22 %, China - 8 %. Interestingly, the pioneers mobile communication in the face of the UK and the US will fall behind countries such as Austria, Ireland and Greece.
Perhaps in a few years we will witness how the group users of traditional and cellular phones are almost equal in number. By the way, today, worldwide, there are about 1 billion wired telephone lines. Because there are already enough reasons to doubt the usual superiority of the wired telephone communication, foreign analysts begin to examine cellular communications as a service equal to wired, and some even give her the championship.
a thriving global market for cellular services attracts the attention of many companies. For example, in Russia, the business involves about two hundred operator companies. Everything is speeding up the pace of development of society strongly require more personalized services, namely: opportunities telephone conversation (and not only) with any party, in any place and at any time. Note that last phrase became, indeed, in our days the motto cell connection. And not just her.
Now a more detailed look at the components of the cellular market and some historical phases, both technical and organizational her the formation. But first a little digression.
On the basis
Affecting a great theme, it is useful to begin with the terminology, so a little organize the knowledge that readers managed to get previously from other sources, and also to delineate the boundaries of the narrative.
In connection with the above, first, we note that cellular communication is the kind of high-mobility radio, differing primarily in the mass customer service in a limited area. While historically it happened so that mobile communication has gradually expanded the scope of service telephone network (PSTN). Actually, the term "cellular" is the accepted abbreviation services obtained through deployed cellular mobile communication networks, one based on the relevant systems. Thus, this term characterizes a movable connection. Such long arguments necessary to distinguish the cellular network and cellular communications, for the first refers to the manner of exercise of the coverage of a certain area (respectively, can be used to provide services like mobile, so and fixed networks) and the second service in the form of transmission and reception of information solely between mobile subscribers of the cellular network. And today, it can not only speech, but also data, of course, and the Internet.
It should be remembered that any radio system, working with subscriber the radio terminal having a non-directional antenna, is in one way or another degree mobile (and only when rigid fixation of the antenna movement of the subscriber impossible), because the user can navigate within the zone of action of base station (BS) and maintained it. Therefore, such a communication system can be divided into those that serve inactive subscribers with the ability to navigate during a communication session only within the zone service one BS (these systems are rather fixed), and those that allow highly mobile subscriber to perform the continuous session connection when moving (including very fast, even at a speed of 100 km/h and more) from the service area of one BS to another area BS and forth across the territory covered by the network. This is the actual cellular.
From the foregoing it can be concluded that the notion of "fixed link" here is often used incorrectly, and if the radio system consists only of one base station with a large radius of action, it usually can to provide a mobile radio communication in its service area. If the underlying station to be located at the satellite, then we will take an important step towards the creation of network global (planetary) satellite communications. But go down to the ground and now we will "cells".
The name of the cellular network in accordance with a cellular principle communication, which is as follows. In the service area of cell the network sets the required number of the already mentioned basic transceiver stations (BS), each of which has a relatively a small area of coverage, several overlapping the service area of a neighboring BS (to provide continuous radio coverage areas). Responding to emerging the reader logical question: "Why?", - many authors of works on cell communication is often cited similar arguments: "to ensure subscribers opportunities to move", "to carry electromagnetic compatibility neighboring cells "them" to improve the quality of communication". All this, of course, true, but, first, in a good interest coverage and network operators fixed-line and, secondly, objectively any network operator always concerned that his network would contain smaller cells. And even better that the network generally consisted only of one cell, because it is the most simple and cheap.
Another thing is that to implement this usually fails and when I try the simultaneous maintenance of a significant number of subscribers, grouped on a relatively small area, there is inevitably a need for the appropriate number of radio channels of communication. As the radio spectrum is as known operated by many users of a natural resource which always never enough. Including those who organize many radio interfaces between base stations and subscriber terminals (cell phones).
Thus, the main challenge facing any network, is economical reuse the same radio frequency resource, the selected network operator to reach the largest possible number of subscribers. This the approach allows for serious commercial level to solve the problem really queueing subscribers.
About the benefits of bees
Now a few words about the cells or, as they are called cells. Why, by the way, honeycomb? Yes, because the coverage area around the BS in the General case is a circle. And equilateral shapes inscribed in a circle (triangles and squares do not count), only the hexagons can without breaks to cover any surface. Therefore, they are used as mathematical models of the cellular network. It is also clear that at the time much before radio operators guessed bees. The size of cells/cell cell radiotelephone network in practice can range from tens of meters to tens of miles, however the smallest of their species are organized in special places clusters of subscribers (for example, business centers), often named according to their size: Pico - or microcells. For the purpose of increasing subscriber capacity of a cell can to run in a multi-sectoral performance (usually three or six sectors), which is equivalent to cost-effective organization is one cell, respectively, three or six. In this case, the BS represent a block of several transceivers, each with its directional antenna serves the relevant sector of a cell. It remains to add that one cell of the cellular network together with installed BS foreign specialists usually referred to as "cell site".
A very important task facing the operator of many cellular networks any purpose, the RF planning SOT. Indeed, if the technology of the radio interface of the cellular network provides for the separation of radio channels by frequency, the neighboring cells can not operate on the same radio frequencies and reuse them, stepping back a certain distance, depending on the specifications of BS. This situation is very common, but very unpleasant for the operator, because the need for a new cell leads due to the high frequency of rescheduling extensive network fragments. However, such problems do not disturb everyone. Tell about it later.
In pursuit of the subscriber
Next very important I. say even defining the term in cellular this so-called relay control transfer between cells when moving subscriber from one cell to another. It is this ability distinguishes cellular from a wireless connection at all. This control is provided not BS, and specialized switching center, which is the core of the network and to which connected all the BS, While the center, representing in General specialized PBX. included in Tfol. Switching control is associated with the organization of a new channel of communication and the transfer to it of the particular telephone connection. It can be made in different ways, called "hard" or "soft", which depend on the used network technology and will be considered below. We still dwell only on the name.
Historically, in Europe the process of switching more often called "hand-over",and in North America - "hand-off". Therefore, meeting these discrepancies, one should not be surprised. Considering the hand-off (we stop for a shorter name), it is impossible to ignore the case when a subscriber moves from one service area of the cellular network at area service of any other. But different networks have different owners-operators. Process (a also a possibility) implementation of control transfer between cells/networks of different owners not only received abroad called "roaming" (rogue), but firmly established in the Russian-language writing as "roaming".
Of course, on the one hand, and the hand-off is nothing like roaming between adjacent cells, however, communicators mean by roaming much more, and - inter-operator interaction, for which, of course, not only must match the technical specifications and standards networks, but should be appropriate agreements on tariff policy, mutual settlements and D. moreover, the cellular network may not be adjacent to each other, which indicates that roaming is the ability to receive services in other networks operators (with which it has contracts for services) with one and the same cell phone. It remains to add that roaming charges can be automatic when the process of transition from one operator to another subscriber notice only relevant display on the user's terminal, right on received account. Non-automatic roaming preliminary the notification of the operator to the subscriber an opportunity to travel outside the network with all the attendant inconveniences, the degree of which depends on quickness and facilities of the operator. Well, the most versatile and unobtrusive, but also the uncomfortable roaming - it's just a change cell phone when you travel outside the actions of "their" network. However, if we can't use your subscriber the terminal, then it is not roaming at all (although some operators offer this kind of roaming!).
The technology of the radio interface
Cellular communication is characterized by the possibility of multicostata, which implies the simultaneous transfer of information through one device many users in common channel of communication With the separation channel can be carried out by frequency (FDMA - Frequency Division Multiple Access), time (ТDМА - Time Division Multiple Access) and code (CDMA - Code Division Multiple Access). The features of these technologies clearly shown.
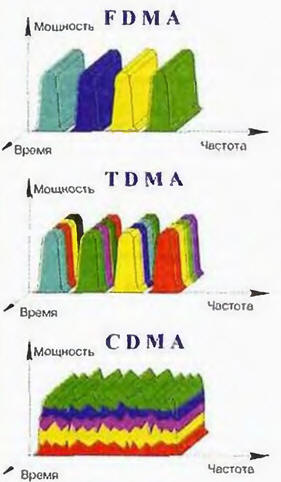
In frequency dividing range transmission is divided into sections devoted to different users. Only this method can be used in analog cellular communication. Therefore, it is based all known analog standards cellular: NMT, AMPS, TACS, etc. Disadvantages of analog systems now obvious: poor noise immunity and the associated low quality speech transmission" inefficient use of scarce radio spectrum, no protection from eavesdropping etc., Should also say that the peak of its development analog systems were back in 1993, after which there is a steady the decline in the number of their subscribers, and in a few years they should even go to the communications market due to the loss of interest on the part of operators and subscribers. The most same common analog standard in the world was and still remains AMPS.
Two other methods are used in digital technologies and, as a rule, in combination with frequency division.
In the case of multicostata with time division multiplexing numerous subscribers pass their messages on the same radio frequency, but at different times that allows you to increase the volume of voice traffic and to obtain other benefits, characteristic of digital communication systems. Based on this method such famous narrow-band digital cellular standards like GSM and its variety DCS, as well as D-AMPS, which is a logical development (improvement) of the standard AMPS. There are even Japanese standards, but their scope is limited exclusively to the national territory.
The principle used in the systems of multicostata CDMA, is to increase the spectrum of the original information signal (in our case, voice) using special signal envelope with a unique shape, which is a kind of code. As can be seen, in this case, all subscribers work for some and the same radio frequencies, resulting in cellular CDMA network, there is no need to spend a lot of efforts for the implementation of frequency planning. In the receiver received on the other side the signal is processed using identical code, the result of which will restore the original information signal. At the same the time signals of the other users for a given receiver continue to stay extended and perceived them only as "white noise", which is the most "soft" obstacle, in the least degree interfere with normal operation of the receiver. Of course. to this we shall return. And so popular to explain the principle of operation of such a system, let us turn to a very good allegory "for experts and not very", that is, explaining the basics of CDMA technology, usually offers Motorola. Imagine a room in which simultaneously talking with each other many pairs of people, and in different languages. Each of they are well aware of his companion, and all extraneous conversations perceived as a background, which is not particularly interfere with conversation. Here, in fact, the whole principle. The case for technology.
Author: A. Golyshko, Moscow






