Below is published a paper by V. Zharkova, host of the London television station in Lviv. This technique is associated with chromospheric flares of the sun, which, in his opinion, form a sporadic layer, and concludes that this technique is possible during high solar activity.
However, the dimensions of the layer Es show that not only is there a direct correlation (coincidence, coherence) between the Es layer and solar activity, and in the last cycle of solar activity was weak inverse correlation.
From 1957 to 1961, despite the fact that the activity fell more than twice, the electron density of this layer remains on the same level.
As you know, chromospheric flares occur from March to September, while distant reception of television is more likely to occur from may to August, during the same period, the electron density of the layer Es, the greatest.
In the summer season chromospheric flares, strongly influencing the ionosphere, are rare - not more than 2-3 times a month, and the high electron density of Es layer is observed almost daily.
Chromospheric flares affect the ionosphere mainly on the illuminated hemisphere, reception of distant TV, though less common, are also possible in the evening and at night.. .
A satisfactory explanation of the nature of Es layer has not been found yet, and the assumption Zharkova T. about the connection of this layer with chromospheric flashes of interest, but require further observation and comparison.
It is well known that long-distance reception of television usually occurs in the summer months and mainly due to the reflection from the ionized layer Es, the structure and origin, which have so far insufficiently understood.
Found that cases of long-distance reception of television broadcasts are repeated every 27 days.
In the graphs (Fig. 1) provides a comparison of the cases of distant TV signals, the London television station (frequency 45 MHz) with solar data: spot number W and a frequency of chromospheric flares X. the Reception of signals was performed on a stationary antenna that focuses on the local television station (Lviv), located about 80 km South of the point of observation (Sokal). Thus the signals of extremely long-range stations were taken as interference with local television program.
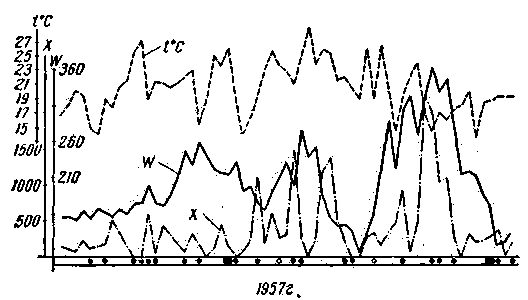
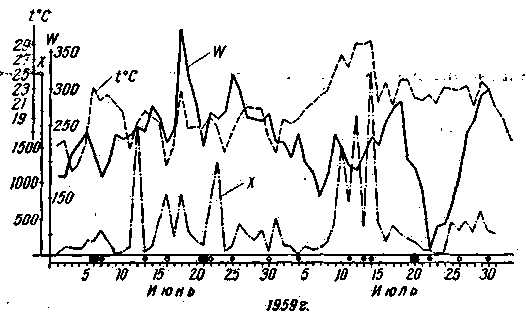
Fig. 1. Comparison of long-distance reception of television programs with chromospheric flashes and spots in June, July, 1957, 1959:
X - chromospheric flares
W - the number of spots
t°C - air temperature in Lviv region
O - the reception of the London television centre (45 MHz)
O. - the reception of Roman telecentre (49 to 56 MHz)
O. - expected (missed) the reception of the London television centre.
As can be seen from the graphs, the incidence of ultra-long reception of the transmission coincides with a repetition rate of chromospheric flares; however, between the beginning of the outbreak and the formation of ionized clouds passing from two to six days. This time the "lag" depends on the average speed of the development of outbreaks from start to maximum (tg HSR) and the average speed of the development of penoobraznaya (tgWcp).
The effect of solar flares on the ionization of the ionosphere is quite reliable fact.
We can assume that the ionizing effect of solar flares have the most pronounced at 23°-14° North for the summer months.
In the years of solar activity minimum frequency of receiving television broadcasts, as well as the duration of appointments will be considerably less.
If we compare the duration of reception of television signals and the total ionizing radiation flares, get the direct dependence. When a large total radiation (10 and 11 June, 22 and 23 June, 3 and 4 July 1957 in Fig. 1) the passage of the television signal was the next day. During a powerful solar flare explosions and there is also a significant increase in air temperature.
In conclusion, it should be noted cases where ultra-long reception was observed in the absence of outbreaks. Indeed,if we apply the rotating antenna and antenna amplifier, ultra-long reception is sometimes possible in the absence of chromospheric flares, however, this technique is very transient and fragile - one of the station being received is replaced by another .etc., This may occur by reflection from meteor trails, and from weakly ionized formations arising from cosmic rays and from weak chromospheric flares.
What years will be the most favorable for long-distance reception of television?
As you know, the previous period of the 11-year solar activity began in 1955, However, the most favorable for long-distance reception of television were 1957, 1958, 1959 and 1960, the years close to solar maximum. Thus, you can expect good conditions for long-distance reception of television in 1967-1968. Lviv.
Author: Vladimir Zharkov; Publication: N. Bolshakov, rf.atnn.ru






